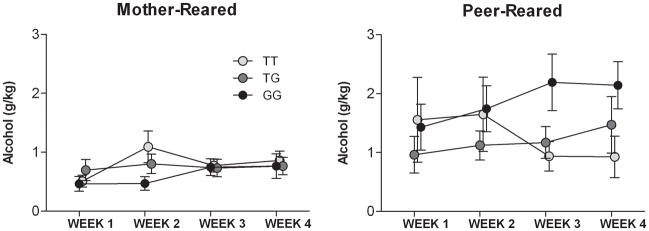
Figure 5. Interaction between rhNPY genotype (T/T, T/G, G/G) and early rearing history (MR, mother- reared, vs. PR, peer-reared) on alcohol consumption over repeated weeks of alcohol deprivation (WEEKS 1, 2, 3, and 4).
There were both genotype by time (F(6, 204) = 3.02, P < 0.008) and genotype by time by rearing time (F(6, 204) = 2.2, P < 0.05) interactions. In PR monkeys, alcohol intake decreased across over time in individuals with the T/T genotype, but an escalation in consumption was observed in those carrying G allele. There was no significant effect of genotype in MR monkeys. The interaction between time and genotype accounted for 19% of the variance in PR monkeys. (MR T/T = 22, MR T/G = 19, MR G/G = 7; PR T/T = 9, PR T/G = 10, PR G/G = 7). Values shown are G/KG alcohol consumed in a 1-hour session (G/KG/H) ± SEM following a 3-day period of deprivation.