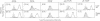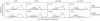Abstract
Gamma delta (gamma delta) T cell receptor (TCR) expressing T cells comprise 3% of human peripheral blood lymphocytes, yet their role in the immune response remains largely unknown. There is evidence both in humans and in animal models that these cells participate in the immune response to mycobacterial antigens. In mice, exposure to mycobacterial antigens leads to the expansion of gamma delta T cells in draining lymph nodes and lungs. In humans, gamma delta T cell lines with reactivity to mycobacterial antigens have been derived from synovial fluid of a rheumatoid arthritis patient, skin lesions of leprosy patients, and peripheral blood of a healthy tuberculin reactor. Very little is known, however, about the factors which induce human gamma delta T cells to expand. In studies comparing the human T cell response to live and heat-killed Mycobacterium tuberculosis (MT), we have found that monocytes infected with live MT are very effective inducers of human gamma delta T cell expansion. After 7 d of exposure to live MT, gamma delta T cells were greatly increased in all healthy tuberculin reactors (PPD+) tested and frequently were the predominant T cell population. In contrast, heat-killed MT or purified protein products of MT induced a CD4+, alpha beta TCR+ T cell response with very little increase in gamma delta T cells. Furthermore, a similar selective induction of gamma delta T cells was observed when monocytes infected with live Salmonella were used to stimulate T cells. Heat-killed Salmonella, like heat-killed MT, induced a predominantly CD4+ alpha beta TCR+ T cell response. These findings suggest that human gamma delta T cells are a major reactive T cell population during the early stages of infection with living intracellular bacteria and are therefore likely to exert an important role in the initial interaction between host and parasite.
Full text
PDF


Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Band H., Hochstenbach F., McLean J., Hata S., Krangel M. S., Brenner M. B. Immunochemical proof that a novel rearranging gene encodes the T cell receptor delta subunit. Science. 1987 Oct 30;238(4827):682–684. doi: 10.1126/science.3672118. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bluestone J. A., Matis L. A. TCR gamma delta cells--minor redundant T cell subset or specialized immune system component? J Immunol. 1989 Mar 15;142(6):1785–1788. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Born W., Happ M. P., Dallas A., Reardon C., Kubo R., Shinnick T., Brennan P., O'Brien R. Recognition of heat shock proteins and gamma delta cell function. Immunol Today. 1990 Feb;11(2):40–43. doi: 10.1016/0167-5699(90)90015-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chang T. W., McKinney S., Liu V., Kung P. C., Vilcek J., Le J. Use of monoclonal antibodies as sensitive and specific probes for biologically active human gamma-interferon. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1984 Aug;81(16):5219–5222. doi: 10.1073/pnas.81.16.5219. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ellner J. J., Schacter B. Z., Bhe F. T. Tuberculin response of lymphocytes from human skin test nonreactors; evidence for in vitro primary sensitization of T lymphocytes. Cell Immunol. 1979 Jun;45(1):213–220. doi: 10.1016/0008-8749(79)90379-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Emmrich F., Thole J., van Embden J., Kaufmann S. H. A recombinant 64 kilodalton protein of Mycobacterium bovis bacillus Calmette-Guerin specifically stimulates human T4 clones reactive to mycobacterial antigens. J Exp Med. 1986 Apr 1;163(4):1024–1029. doi: 10.1084/jem.163.4.1024. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gillis S., Ferm M. M., Ou W., Smith K. A. T cell growth factor: parameters of production and a quantitative microassay for activity. J Immunol. 1978 Jun;120(6):2027–2032. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Haregewoin A., Soman G., Hom R. C., Finberg R. W. Human gamma delta+ T cells respond to mycobacterial heat-shock protein. Nature. 1989 Jul 27;340(6231):309–312. doi: 10.1038/340309a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Janis E. M., Kaufmann S. H., Schwartz R. H., Pardoll D. M. Activation of gamma delta T cells in the primary immune response to Mycobacterium tuberculosis. Science. 1989 May 12;244(4905):713–716. doi: 10.1126/science.2524098. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kabelitz D., Bender A., Schondelmaier S., Schoel B., Kaufmann S. H. A large fraction of human peripheral blood gamma/delta + T cells is activated by Mycobacterium tuberculosis but not by its 65-kD heat shock protein. J Exp Med. 1990 Mar 1;171(3):667–679. doi: 10.1084/jem.171.3.667. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Koga T., Wand-Württenberger A., DeBruyn J., Munk M. E., Schoel B., Kaufmann S. H. T cells against a bacterial heat shock protein recognize stressed macrophages. Science. 1989 Sep 8;245(4922):1112–1115. doi: 10.1126/science.2788923. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lanier L. L., Ruitenberg J. J., Phillips J. H. Human CD3+ T lymphocytes that express neither CD4 nor CD8 antigens. J Exp Med. 1986 Jul 1;164(1):339–344. doi: 10.1084/jem.164.1.339. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Modlin R. L., Pirmez C., Hofman F. M., Torigian V., Uyemura K., Rea T. H., Bloom B. R., Brenner M. B. Lymphocytes bearing antigen-specific gamma delta T-cell receptors accumulate in human infectious disease lesions. Nature. 1989 Jun 15;339(6225):544–548. doi: 10.1038/339544a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moore M. W., Carbone F. R., Bevan M. J. Introduction of soluble protein into the class I pathway of antigen processing and presentation. Cell. 1988 Sep 9;54(6):777–785. doi: 10.1016/s0092-8674(88)91043-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Morrison L. A., Lukacher A. E., Braciale V. L., Fan D. P., Braciale T. J. Differences in antigen presentation to MHC class I-and class II-restricted influenza virus-specific cytolytic T lymphocyte clones. J Exp Med. 1986 Apr 1;163(4):903–921. doi: 10.1084/jem.163.4.903. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- O'Brien R. L., Happ M. P., Dallas A., Palmer E., Kubo R., Born W. K. Stimulation of a major subset of lymphocytes expressing T cell receptor gamma delta by an antigen derived from Mycobacterium tuberculosis. Cell. 1989 May 19;57(4):667–674. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(89)90135-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Orme I. M. Induction of nonspecific acquired resistance and delayed-type hypersensitivity, but not specific acquired resistance in mice inoculated with killed mycobacterial vaccines. Infect Immun. 1988 Dec;56(12):3310–3312. doi: 10.1128/iai.56.12.3310-3312.1988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Patel S. S., Wacholtz M. C., Duby A. D., Thiele D. L., Lipsky P. E. Analysis of the functional capabilities of CD3+CD4-CD8- and CD3+CD4+CD8+ human T cell clones. J Immunol. 1989 Aug 15;143(4):1108–1117. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Raulet D. H. Immunology. Antigens for gamma/delta T cells. Nature. 1989 Jun 1;339(6223):342–343. doi: 10.1038/339342a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rivas A., Koide J., Cleary M. L., Engleman E. G. Evidence for involvement of the gamma, delta T cell antigen receptor in cytotoxicity mediated by human alloantigen-specific T cell clones. J Immunol. 1989 Mar 15;142(6):1840–1846. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Spits H., Borst J., Tax W., Capel P. J., Terhorst C., de Vries J. E. Characteristics of a monoclonal antibody (WT-31) that recognizes a common epitope on the human T cell receptor for antigen. J Immunol. 1985 Sep;135(3):1922–1928. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]