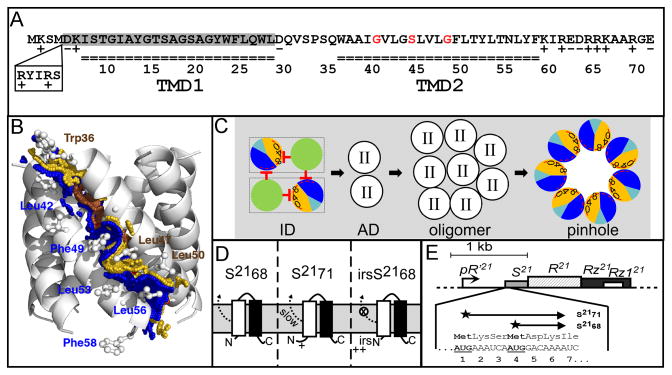
Figure 1. A. Features of S21.
The amino acid sequences encoded by S21 are shown. S2171 and S2168 sequences begin at Met1 and Met4, respectively. Residues in each transmembrane domain are underlined. The residues deleted in S2168ΔTMD1 are shaded in gray. The glycine zipper (Gly40, Ser44 and Gly48) is colored in red. The position and sequence (RYIRS) of the irs epitope in irsS2168 are shown in the box.
B. Side view of the pinhole model.
The modeled helix-helix contact surfaces are shown. Surface A (W36A37xxG40V41xG43S44xxL47G48xL50T51xxT54) is colored in gold and labeled in brown, and contains the glycine zipper (Gly40, Ser44 and Gly48), colored brown. Contact surface B (A38xxV41L42xxL45xxxF49xxY52L53xN55L56xF58) is shown and labeled in blue. Adapted from Pang et al (2009) with permission.
C. Model of S2168 hole formation pathway (top-down view from periplasm).
The two TMDs (green: TMD1; sectored: TMD2) in a single S2168 molecule are boxed. Initially, both TMDs are inserted in the membrane in an inactive dimer (ID) form, with TMD1 inhibits TMD2 both in cis and in trans. Then both TMD1s are released, which converts the inactive dimer into an activated dimer (AD) form. Activated dimers then aggregate into oligomers, and nucleate to form heptameric pinholes. In TMD2, orange and dark blue represent A and B interaction faces (Fig. 1B), with 0, 4, and 8 indicating the helical positions of the G40, S44, and G48 residues, respectively. The red stop arrows indicate the cis and trans inhibition of TMD1 to TMD2. The interaction face(s) of TMD2 in both the activated dimer and oligomer are not shown; TMD2 is depicted as clear circle with roman numeral II in both cases. The hydrophilic and weakly hydrophobic residues of TMD2 that eventually face the lumen of the pinhole are represented by a red arc. Grey, lipid. Modified from Pang et al (2009) and (2010) with permission.
D. The membrane topology of S2168 (left), S2171 (middle), and irsS2168 (right). TMD1: white box; TMD2: black box. The TMD1 of S2168 is initially inserted in the membrane but later released into the periplasm (Park et al., 2006). The externalization of TMD1 is delayed in the context of S2171 and completely blocked in the context of irsS2168. Adapted from Pang et al (2010) with permission.
E. The phage 21 lysis cassette.
The phage 21 lysis genes S, R, Rz, and Rz1 are located downstream of the late gene promoter pR′21. S21 gene has a dual-start motif, which encodes both a holin S2168 (translated from Met4), and a weak antiholin S2171 (translated from Met1). Both start codons are bold underlined. Adapted from Pang et al (2010) with permission.