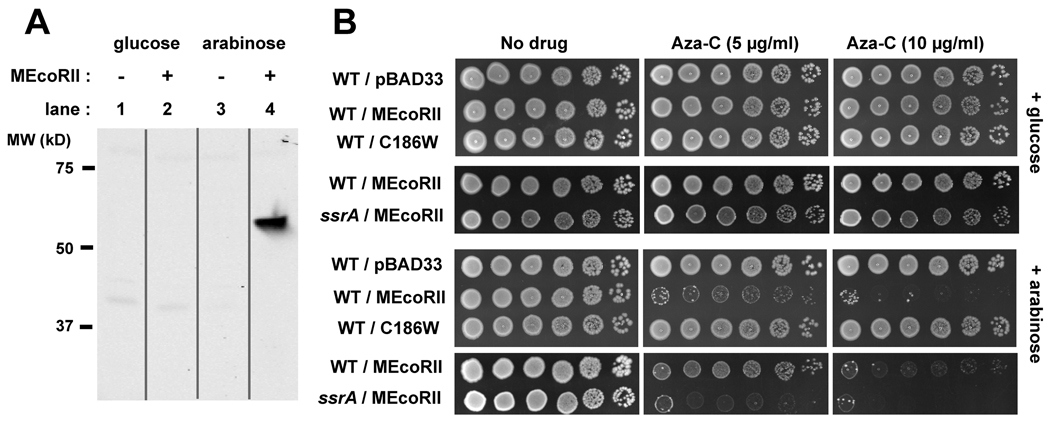
Figure 3. Arabinose-inducible M.EcoRII expression results in aza-C sensitivity.
In panel A, extracts from HK21 cells with or without M.EcoRII plasmid pBAD-MEcoRII were analyzed by Western blotting. The cells were pre-grown with glucose for 1.5 generations, pelleted and washed with fresh LB, and then resuspended in LB containing glucose (0.2%) or arabinose (0.05%). Protein was extracted after 60 minutes of incubation at 37°C. In panel B, overnight cultures of HK21 (WT) or the ssrA derivative of HK21 (ssrA), with the indicated pBAD33-derived plasmid, were diluted to approximately 4 × 108 cells/ml. Ten-fold serial dilutions were generated across a microtiter plate and 5 µl of each dilution was spotted onto LB plates with no drug or the indicated concentration of aza-C. The upper panels are plates that contained glucose (0.2%), while the lower panels are plates that contained arabinose (0.05%). Plates were photographed after overnight incubation at 37°C. The experiment comparing different M.EcoRII plasmids (panels with 3 rows) was done on a different day than the one comparing wild-type and ssrA mutant cells (panels with 2 rows); the latter plates were incubated for several hours longer to allow good growth of the ssrA mutant in the absence of aza-C. This may account for the somewhat weaker inhibition of the wild-type with M.EcoRII in row 9 compared to row 7 (however, we also detect some day-to-day variation in apparent aza-C potency in plates, perhaps due to aza-C instability).