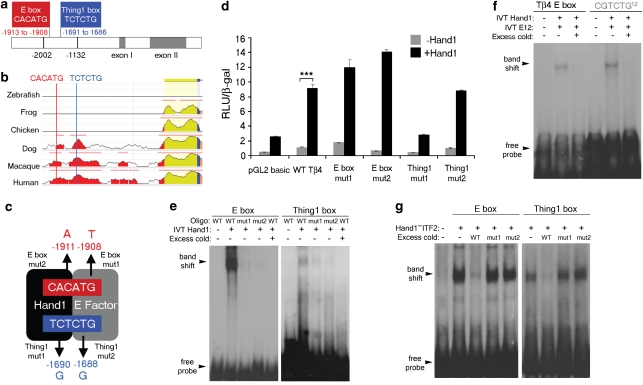
Figure 1. Hand1 is a transcriptional regulator of Tβ4.
A consensus E-box (CACATG, in red) and Thing1 box (TCTCTG, in blue) are found within a regulatory region upstream of the Tβ4 promoter (a). Sequence alignment reveals that the Hand1-binding sites proximal to the Tβ4 promoter are conserved in mammals. Evolutionarily conserved regions are indicated by coloured peaks and represent at least 100 bp of sequence and 70% identity; red peaks represent upstream intergenic regions; yellow peaks represent untranslated regions; blue peak is the first exon of Tβ4 and the salmon region is the intronic sequence (http://ecrbrowser.dcode.org/; (b)). Schematic to illustrate point mutations introduced into the respective half-sites of E-box and Thing1 box; numbers refer to the nucleotide location of each point mutation relative to the ATG of Tβ4 (c). An 870-bp fragment containing the regulatory sequences was placed upstream of a luciferase reporter to assay for transcriptional activity. Luciferase reporter assays indicate a 10-fold activation of a Tβ4 reporter construct by Hand1 (***P<0.001, Student's t-test) (d). Electrophoretic mobility shift assays demonstrate binding of Hand1 to both the E-box and Thing1 boxes within the Tβ4 proximal regulatory sequence, which is abolished by point mutation of E-box residues and severely diminished by point mutation of the Thing1 box (e). EMSA binding of Hand1 and E12 to the E-box within the Tβ4 proximal regulatory sequence compared with an optimal Thing1 Box12 (f). Binding of E-box and Thing1 boxes by a tethered Hand1-E-factor (Hand1–ITF2) heterodimer is not competed away by mutant oligonucleotides (as depicted in (c)) containing a point mutation in the half sequence for either E-factor or Hand1 binding (g); IVT controls of empty vector alone are shown in the left-hand lanes for each of e–g. Error bars in d are s.e.m. of n = mean of three separate transfection experiments, with triplicate wells for each treatment per experiment. IVT, in vitro-translated; RLU, relative light units.