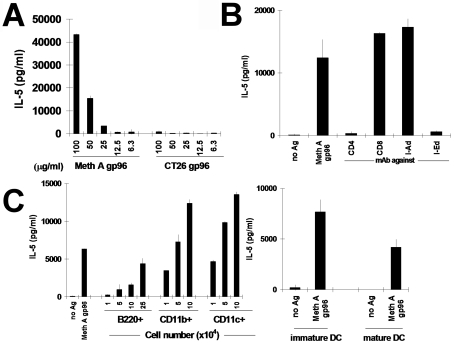
Figure 1.
APCs process and present naturally-derived gp96-peptide complexes to CD4+ T cells in a source-specific manner. Data for clone 24D3 are shown; clone 12D1 behaves similarly. (A) 24D3 cells (2 x 104 cells) and irradiated splenic APCs (5 x 105 cells) were cultured with gp96 derived from either Meth A or an antigenically distinct tumor (CT26) at the concentrations indicated. Secretion of IL-5 by T cells was measured. (B) Stimulation of 24D3 by Meth A gp96 (100 µg/ml) is CD4-restricted, I-Ed restricted, but not CD8-restricred or I-Ad-restricted. Assays were done as in A and monoclonal antibodies against CD4, CD8, I-Ad, or I-Ed (2.5 µg/ml) were added. (C) Identity of splenic APCs. Splenic APCs were tested for MHC II-mediated antigen presentation of Meth A-derived gp96. CD4+ T cell clone 24D3 cells (2 x 104) were cultured with either 5 x 105 irradiated syngeneic splenic APCs or 104, 5 x 104 or 105 CD11b+, CD11c+, or B220+ cells purified from splenic APCs by MACS™ column, in the presence or absence of gp96 derived from Meth A or CT26 (100 µg/ml), as a negative control. For B220+ APCs, an additional titration of 2.5 x 105 cells was tested because of the relative inefficiency of these APCs in re-presentation. Bone-marrow derived immature DCs or mature DCs (1 x 105) were also tested in a similar manner as APCs.