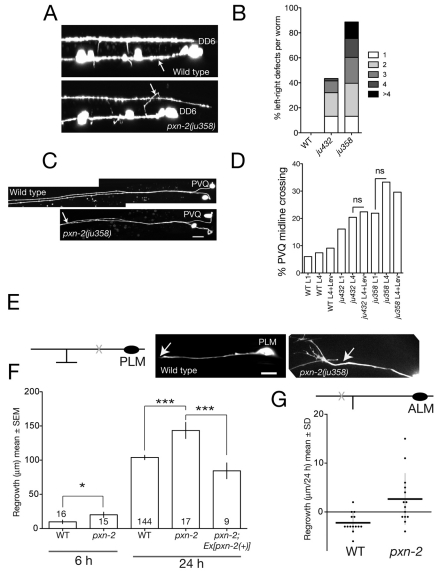
Fig. 6.
PXN-2 functions in selective motoneuron axon guidance choice, prevents midline crossing and inhibits touch neuron axon regrowth after laser axotomy. (A) In wild-type L1 stage C. elegans (Punc-25-GFP, juIs76), commissures of motoneurons DD2-6 extend on the right-hand side. In pxn-2(ju358), commissures frequently extend on the left-hand side (arrow, DD6 commissure). (B) Summary of D neuron commissure handedness defects. The number of commissures that extended incorrectly is shown (n>50 per genotype). (C) Wild-type PVQ axons are fasciculated in the posterior and separate in the anterior. In pxn-2(ju358) animals, PVQ axons inappropriately fasciculate; oyIs14. (D) pxn-2 midline crossing defects do not increase during postembryonic development. Quantitation in L1 and L4 stage animals and in L4 animals reared on levamisole (Lev) plates. n>45 per group; ns, not significant (Fisher's exact test). (E) (Left) Diagram of PLM neuron showing position of axotomy (X). (Right) Images of PLM regrowth 6 hours post-axotomy in wild type and pxn-2(ju358); arrow, site of axotomy. Note the growth-cone-like structure in pxn-2. (F) Quantitation of PLM (zdIs5) regrowth in wild type and pxn-2(ju358) at 6 and 24 hours. Sample size is indicated within the columns. pxn-2 mutants displayed increased regrowth at 6 hours (*, P=0.02; Mann-Whitney test). The increased regrowth of pxn-2 mutants at 24 hours is rescued by the PXN-2(+) transgene juEx2140 (***, P<0.001; ANOVA and Tukey's post-hoc test). (G) By 24 hours post-axotomy, the distal process of the ALM neuron retracts slightly in the wild type, whereas in pxn-2(ju358) mutants the ALM distal process displays significantly increased regrowth. Dot plot; horizontal lines indicate the mean. P=0.003, Mann-Whitney test. Scale bars: 10 μm.