Fig. 2.
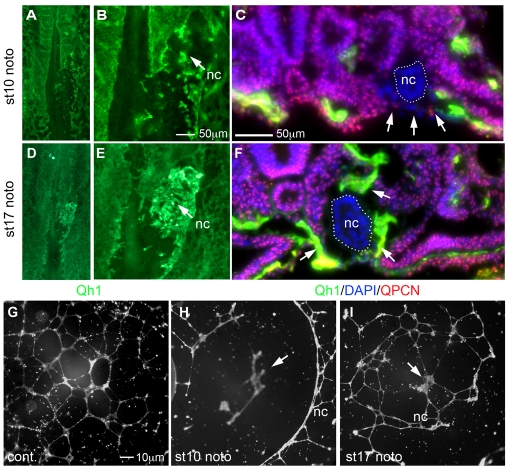
Pre-fusion- and fusion-stage notochords differentially regulate endothelial cell assembly. (A) Quail embryo with stage 10 pre-fusion chick notochord implantation (nc) stained with Qh1 (green). (B) Higher magnification of A. Pre-fusion notochord inhibited local blood vessel assembly (eight out of nine embryos). (C) Section through the implantation site. Endothelial cells (arrows) are absent on the ventral surface of the embryo under the implanted stage 10 chick notochord (nc, white dots) within the surrounding quail host tissue marked with QPCN (red). (D) As in A but implanted fusion-stage chick notochord (stage 17). (E) Higher magnification of D. Endothelial cells accumulate in high numbers at the implanted site (12 out of 13 embryos). (F) As in C but with implantation of fusion-stage notochord showing endothelial cells directly surrounding the implanted stage 17 chick notochord (arrows). (G) Control human aortic endothelial cells (HAECs) assembled into chords. (H) HAECs assembled at a distance from a co-cultured pre-fusion chick notochord (stage 10) in all experiments (n=9). (I) HAECs assembled directly over a fusion-stage notochord (stage 17) in all but one experiment (n=12). nc, notochord.