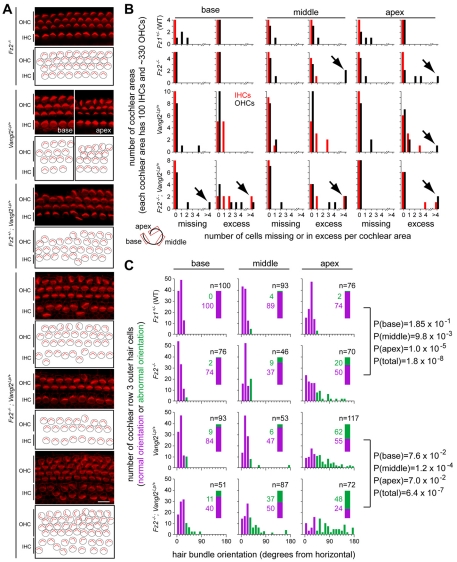
Fig. 6.
Genetic interactions between Fz2 and Vangl2 in auditory hair cell development. (A) Representative phalloidin-stained organ of Corti flat-mounts. The Fz2+/–;Vangl2Lp/+ tissue is P0; all others are E18. Fz2–/– and Fz2+/–;Vangl2Lp/+ images are from the middle cochlea. Images from the base and apex are shown for the Vangl2Lp/+ sample to illustrate the gradient of hair cell misorientation along the cochlea. The three images of a Fz2–/–;Vangl2Lp/+ organ of Corti are from the embryo with the most severe phenotype; they show inappropriate numbers, mislocalization and misorientation of hair cells in the middle (upper two panels) and apex (lower panel) of the cochlea. Beneath each image is a schematic showing hair cell locations and hair bundle orientations. IHC, inner hair cells. OHC, outer hair cells. Scale bar in bottom panel: 10 μm. (B) Quantification of hair cell number in territories of 100 IHCs and ∼330 OHCs sampled from the base, middle and apex of the cochlea at E18, as shown in the schematic in the lower left corner. Red bars, IHCs. Black bars, OHCs. Black arrows highlight deviations of greater than 4 cells. (C) Quantification of OHC3 hair bundle orientations. Based on a 95% cut-off in the distribution of hair bundle orientations observed in the Fz1+/– control (upper row), orientations were divided into `normal' (purple) or `abnormal' (green) groups. For each region (base, middle or apex) and genotype, the number of hair cells in each category is shown with the green and purple rectangular insets. The corresponding P-values (Fisher's two-tailed exact test) for comparisons between genotypes that differ by the presence or absence of Fz2 are shown to the right.