Fig. 4.
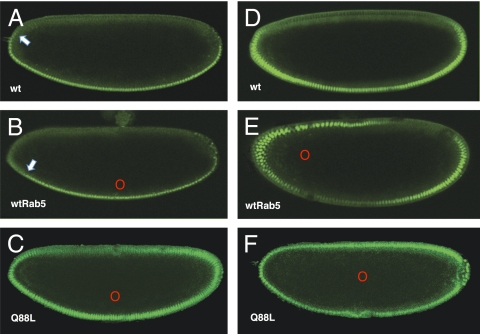
(A) Mock-injected control embryo expressing Dorsal-GFP showing the WT (wt) Dorsal gradient. The Dorsal gradient is retracted toward the ventral midline (arrow). (B) Dorsal-GFP–expressing embryo injected near the ventral midline with synthetic mRNA encoding WT Rab5 (red circle). The Dorsal gradient is retracted toward the ventral midline (arrow). (C) Dorsal-GFP–expressing embryo injected ventrolaterally (red circle) with mRNA encoding constitutively active Rab5Q88L. The Dorsal gradient is expanded dorsolaterally but exhibits normal polarity. (D) Mock-injected Dorsal-GFP control embryo viewed at the same relative ventrolateral position as the embryo in E. (E) Dorsal-GFP–expressing embryo injected with synthetic mRNA encoding WT Rab5 axially at 25% egg length (red circle). The Dorsal gradient is shifted away from the ventral midline toward the site of injection only at the anterior of the embryo. (F) Dorsal-GFP–expressing embryo injected centrally (red circle) with synthetic mRNA encoding Rab5Q88L. Dorsal accumulates in all nuclei. In all cases, ventral is down, dorsal is up, red circles mark the site of injection, and embryos are in nuclear cycle 14.