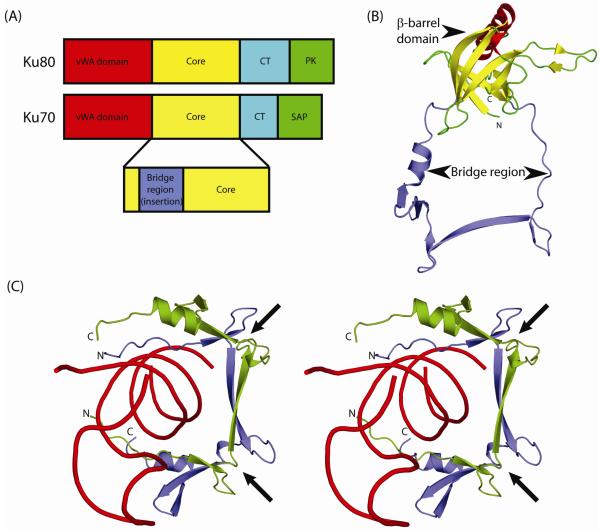
Figure 1.
Domain architecture of Ku.
(A) Eukaryotic Ku is a heterodimer of two similar polypeptides Ku70 and Ku80. Both proteins share a conserved core region (yellow) in addition to an N-terminal von Willebrand factor (vWA; red) domain and a C-terminal helical (CT; cyan) domain. Ku80 contains a C-terminal protein kinase recruitment domain (PK; green) while Ku70 has a SAP domain (green) implicated in DNA binding. Most prokaryotic and bacteriophage versions of Ku contain only the core domain.
(B) Ribbon representation of the human Ku70 core domain (PDB: 1jeq chain A). The Ku core domain is a seven-stranded β-barrel that contains a long insertion, between its second and third β-strands, termed the bridge-region. The β-strands of the β-barrel domain are colored yellow and the bridge region is colored blue.
(C) Stereo ribbon diagram of the dsDNA-encircling bridge-region of human Ku heterodimer (PDB: 1jey). The bridge-regions of Ku70 and Ku80 are colored blue and green respectively, with dsDNA colored red. Arrows indicate the locations of the deteriorated Zn-binding sites.