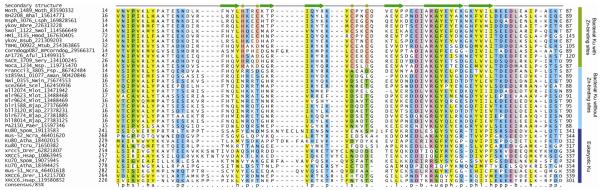
Figure 2.
Multiple sequence alignment for representative proteins of the Ku superfamily. The first and last residue numbers are indicated before and after each sequence in the alignment. Excluded residues are specified as numbers. The secondary structure diagram based on the crystal structure of the human Ku70/Ku80 (PDB: 1jeq) dimer is indicated above the alignment and the constituents of the Zn-binding site are indicated as green circles. The alignment has been colored as per the 85% consensus, with ‘h’ being hydrophobic, ‘l’ the aliphatic subset thereof, ‘p’ being polar, ‘s’ being small, ‘−‘ being negatively charged, ‘+’ being positively charged, b being bulky, u being tiny and ‘a’ being aromatic residues. The Zn-binding positions are shaded differently in the proteins in which the Zn-chelating residues are retained. The organism abbreviations are -- Aful : Archaeoglobus fulgidus; Aman : Aurantimonas manganoxydans; Atha : Arabidopsis thaliana; BPCorndog : Mycobacterium phage Corndog; Bbre : Brevibacillus brevis; Bhal : Bacillus halodurans; Bjap : Bradyrhizobium japonicum; Bsub : Bacillus subtilis; Drer : Danio rerio; Fsp. : Frankia sp.; Hmod : Heliobacterium modesticaldum; Hsap : Homo sapiens; Lsph : Lysinibacillus sphaericus; Mlot : Mesorhizobium loti; Moth : Moorella thermoacetica; Mtub : Mycobacterium tuberculosis; Ncra : Neurospora crassa; Nsp. : Nocardioides sp.; Nwin : Nitrobacter winogradskyi; Paer : Pseudomonas aeruginosa; Scel : Sorangium cellulosum; Sery : Saccharopolyspora erythraea; Spom : Schizosaccharomyces pombe; Swol : Syntrophomonas wolfei; Tcru : Trypanosoma cruzi