Fig. 5.
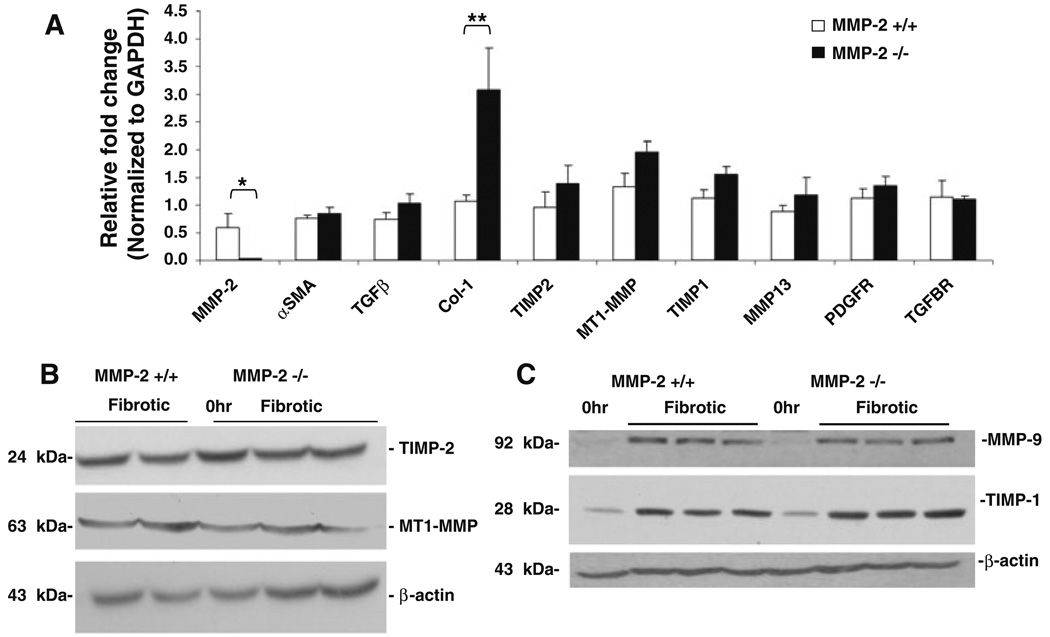
Increased levels of α1(I) collagen mRNA in MMP-2−/− mice after chronic liver injury. Following chronic CCl4 administration, total RNA extracted from MMP-2+/+ and MMP-2−/− mouse livers (n = 4) was reverse-transcribed and real-time PCR analysis was performed to compare expression of “profibrotic genes” as well as genes relevant to MMP-2 activity and function (a). Of all the genes examined only α1(I) collagen mRNA expression was significantly increased (approximately threefold) in the MMP-2−/− group as compared with wild-type control. Results normalized to GAPDH. Data represent means ± SEM; * P < 0.05, ** P < 0.02. b–c Expression of TIMP-1, TIMP-2, MT1-MMP, and MMP-9 examined by immunoblot using whole liver protein extract collected from MMP-2+/+ and MMP-2−/− mice after chronic CCl4 administration. No significant difference in protein expression of molecular regulators of MMP-2 activity (b), MMP-9, a type IV collagenase with substrate specificity similar to MMP-2, or TIMP-1, tissue inhibitor of type I collagenase activity (c) was noted. Expression normalized to β-actin. Representative immunoblots shown