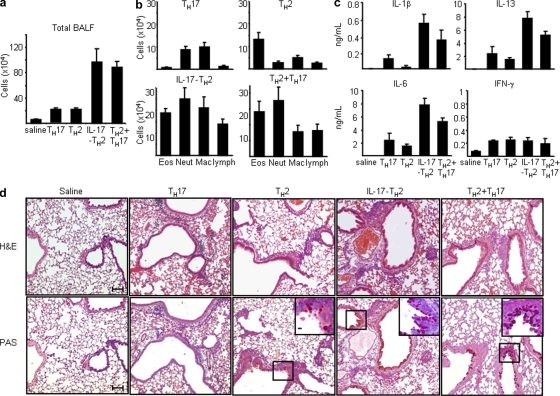
Figure 8.
Antigen-specific inflammatory IL-17–producing TH2 cells promote the exacerbation of allergic asthma. Five groups of BALB/c mice were intranasally challenged once a day for 2 d with OVA 24 h after being adoptive transferred with 0.9% saline as a control or OVA-specific IL-17–producing TH2, classical TH2, classical TH17, or classical TH2 and TH17 cells generated in vitro, as described in Materials and methods. BALF of individual mice of each group were collected for the measurement of total cell counts (a) and differential cell counts (b), indicating that the total numbers of individual inflammatory cells in each group or (c) concentrations of indicated cytokines by ELISA. (d) Histological analysis of representative lung bronchovascular bundles stained with hematoxylin and eosin (H&E; top) or stained with periodic acid Schiff (PAS; bottom). The insets at the corner depict higher magnification images of the airway epithelium stained with PAS, showing that much more abundant mucus-producing cells (pink cytoplasm) are lining the airway epithelium of mice receiving indicated T helper cell subsets. Data are representative of three independent experiments. Data represented as the mean (±SD); four mice per group. Bars: (capped) 100 µm; (uncapped) 10 µm.