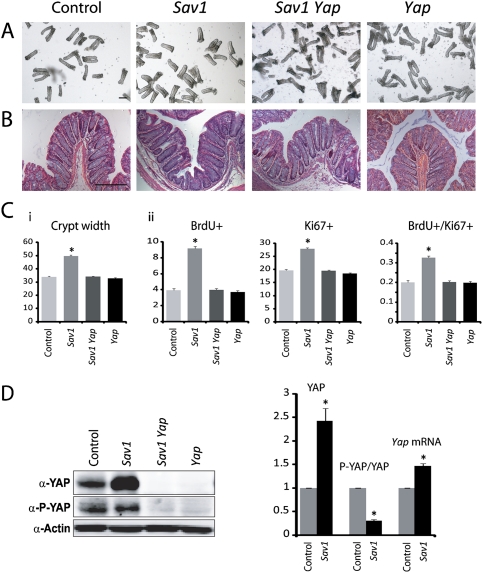
Figure 3.
Loss of Sav1 results in Yap-dependent crypt hyperplasia. (A) Isolated colonic crypts from 4-wk-old wild-type, Sav1, Yap, or Sav1 Yap double-mutant colons. Note the enlarged width of Sav1 mutant crypts. Quantification of crypt width is shown in C, graph i. (B) H&E staining of the colonic sections from 4-wk-old wild-type, Sav1, Yap, or Sav1 Yap double-mutant colons. Note the enlarged width of Sav1 mutant crypts. (C, graph i) Quantification of crypt width from A. Eighty crypts from three mice of each genotype were used. Data are mean ± SEM. (*) P < 0.01, t-test. (Graph ii) Quantification of cell proliferation. Four-week-old wild-type, Sav1, Yap, or Sav1 Yap double-mutant mice were analyzed for BrdU and Ki67 staining 2 h after a single i.p. injection of BrdU. The number of BrdU+ or Ki67+ cells and the ratio of BrdU+/Ki67+ in each crypt were quantified with 200 crypts from three mice of each genotype. Data are mean ± SEM. (*) P < 0.01, t-test. (D) Quantification of YAP protein and mRNA levels. Note the increased YAP protein and mRNA levels in Sav1-deficient crypts. Also note that, while the absolute amount of P-YAP was similar in wild-type and Sav1-deficient crypts, the P-YAP/YAP ratio was decreased in Sav1-deficient crypts. Data used in the graph are mean ± SD. n = 3. (*) P < 0.01, t-test. Bars, 100 μm.