Figure 2.
Signal transduction systems for the adaptive response to osmotic stress in yeast and mammalian cells.
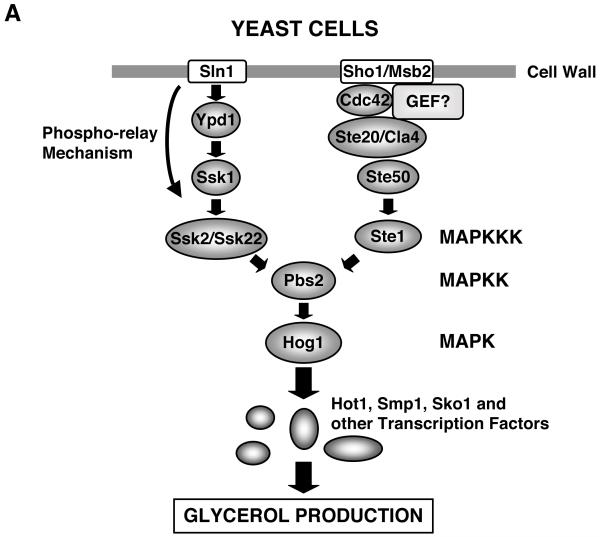
A: Intracellular signaling system for sensing and responding to extracellular hyperosmolarity in yeast.
Yeast cells have two branches (Sln1 and Sho1 branches) for transducing extracellular osmotic stress signal into the nucleus. Extracellular hyperosmolarity is sensed by the cell surface receptors Sln1 and Sho1/Hkr1-Msb2, respectively, and the evoked signal is transduced by multiple intermediate molecules, stimulating Pbs2 and its downstream Hog1 kinase. Hog1 kinase further activates transcription factors Hot, Smp1, Sko1, finally accumulating the osmolyte glycerol inside the cells. Note that the small G-protein Cdc42 plays a role in the Sho-1 branch-mediated signal transduction. Hog1 is a yeast ortholog of the mammalian p38 MAPK.
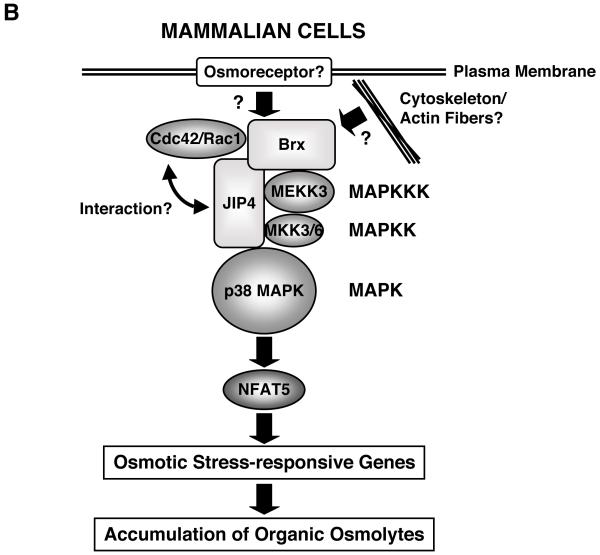
B: Intracellular signaling system for sensing and responding to extracellular hyperosmolarity in mammalian cells.
Upon exposure to extracellular hyperosmolarity, mammalian cells activate a signaling cascade similar to that of yeast, which consists of small G-proteins, p38 MPAK and NFAT5, to induce osmostress-responsive genes and accumulation of several organic osmolytes.
Brx plays a key role in mediating the signal of extracellular hyperosmolarity, sensed by yet undiscovered osmoreceptors and/or alterations in the cytoskeleton, to a downstream signaling cascade by forming a complex with small G-proteins, JIP4, p38 MAPK and its upstream kinases to finally activate NFAT5 and through it to stimulate the transcription rates of osmotic stress-responsive genes.
GEF: guanine nucleotide-exchange factor, HOG1: high osmolarity glycerol 1, JIP4: JNK-interacting protein 4, MAPK: mitogen-activated protein kinase, MAPKK: MAPK kinase, MAPKKK, MAPK kinase kinase, MEKK3: MAPK/ERK kinase kinase 3, NFAT5: nuclear factor of activated T-cells 5