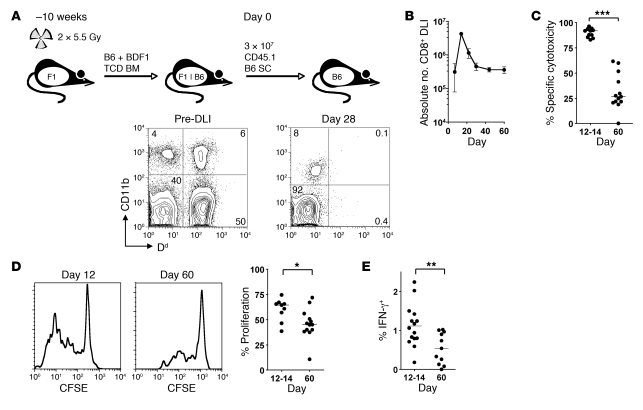
Figure 1. CD8+ T cells transferred to established mixed chimeras show transient cytotoxicity followed by loss of effector function.
(A) Allogeneic chimeras were generated by lethal irradiation of recipient BDF1 (F1) mice followed by reconstitution with T cell–depleted (TCD) B6 and BDF1 BM. 10 weeks later, 3 × 107 CD45.1+ B6 SCs were transferred to established chimeras. A representative example of blood chimerism of mice before and 28 days after DLI is shown using Dd as a marker of BDF1-derived cells. (B) Absolute number of CD45.1+ CD8+ T cells recovered from the spleen at various times following DLI (n = 3 per group per time point). (C) A 1:1 mix of CFSEhi and CFSElo labeled B6 and BDF1 B cells, respectively, were injected intravenously into mice 12 or 60 days after DLI. In vivo cytotoxicity was measured by the disappearance of injected BDF1 B cells relative to B6 B cells after 15 hours. (D) SCs isolated from recipients at 12 or 60 days were CFSE labeled and stimulated for 5 days with irradiated BDF1 SCs. Shown are representative histograms of proliferation of transferred CD8+ T cells and summary data of the percentage of cells that had divided 2 or more times. (E) SCs were restimulated overnight with irradiated BDF1 SCs, and production of IFN-γ by donor CD8+ T cells was measured by intracellular cytokine staining and flow cytometry. Scatter plot indicates the percentage of CD45.1+ CD8+ T cells secreting IFN-γ. *P < 0.05, **P < 0.01, ***P < 0.001, Mann-Whitney test.