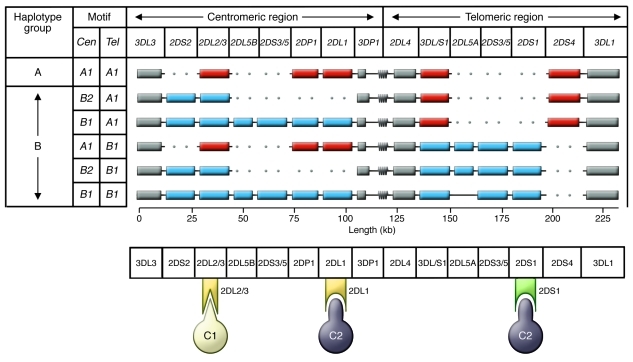
Figure 1. The human KIR locus consists of centromeric and telomeric regions that recombine to produce A and B haplotypes with a distinctive gene content.
Structures of common haplotypes are shown in the top panel. Gray boxes indicate conserved framework genes; red boxes indicate genes characteristic of A haplotypes; blue boxes indicate B haplotype–specific genes. The centromeric (Cen) and telomeric (Tel) gene-content motifs are listed at left. The symbol at the boundary between the centromeric and telomeric regions represents a repetitive sequence, the site for meiotic recombination that has shuffled the centromeric and telomeric motifs. The bottom panel illustrates HLA-C–specific KIRs and their specificities for the C1 and C2 epitopes. Yellow indicates inhibitory receptors KIR2DL2/3 and KIR2DL1; green indicates the activating receptor KIR2DS1.