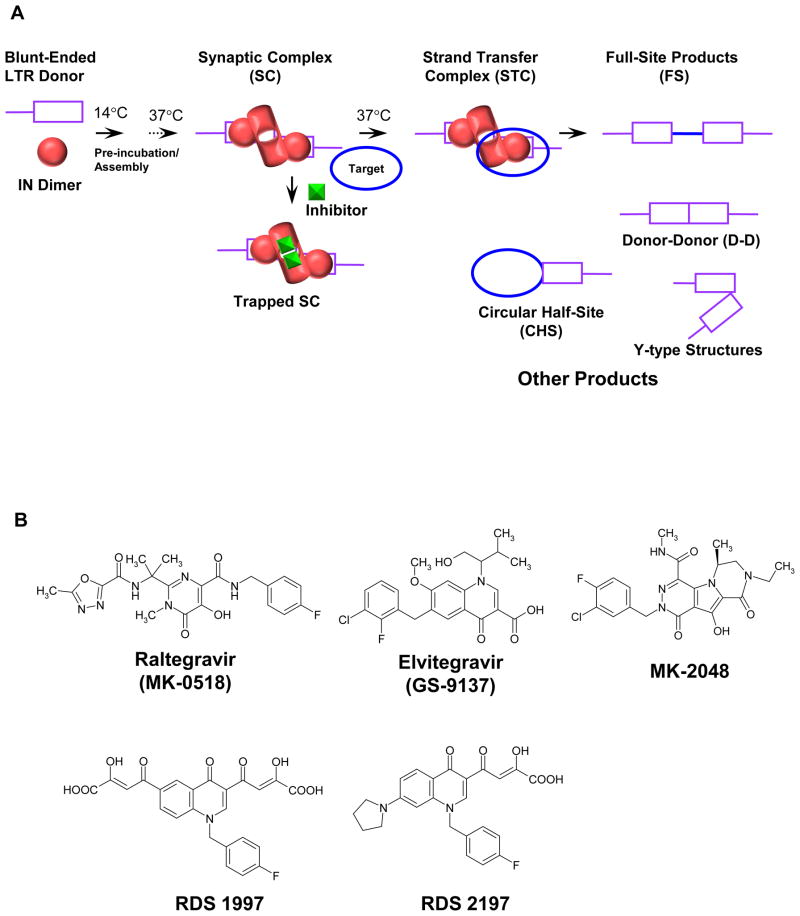
Figure 1.
Schematic for assembly of the SC and the concerted integration reaction. (A) IN dimers assemble onto HIV-1 LTR forming the SC where two LTR ends are non-covalently juxtaposed by IN. The IN dimer bound at each LTR terminus form the active tetramer and is drawn differently to reflect the conformational change associated with 3′-processing of the LTR DNA ends. In the presence of supercoiled target DNA, SC is converted to the STC, the terminal nucleoprotein complex in the concerted integration pathway. STIs prevent target DNA binding to SC resulting in the accumulation of inactivated or trapped SC and thus inhibition of STC formation. Deproteinization of the STC yields the concerted or FS integration product. Other integration products formed in the reaction are CHS, D-D, and Y-type products. (B) Structure of STIs. RDS 1997 is compound 8 in ref (31) and RDS 2197 is compound 6i in ref (32).