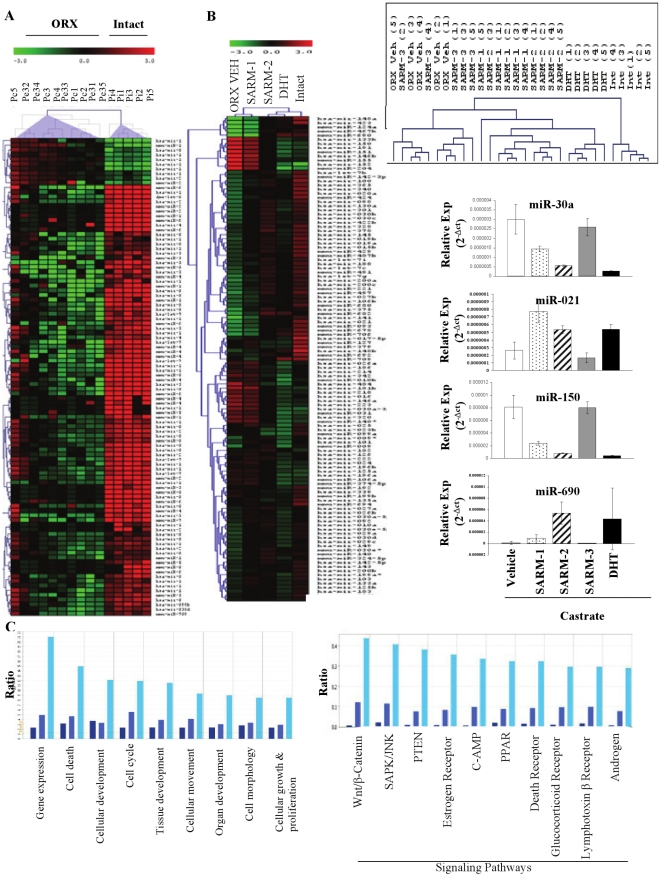
Figure 2. Androgen Receptor ligands alter the expression of miRs in prostate.
A. Castration altered miR expression in prostate. RNA was extracted from prostate of rats that were sham operated (Intact) or castrated (ORX) and treated subcutaneously with vehicle for 14 days. miR expression was profiled using realtime PCR and miRs that are statistically different (P<0.05) between the two groups are expressed in the heatmap. (n = 5). B. Treatment of castrated rats with AR ligands altered miR expression in prostate. Sprague Dawley rats (n = 5; 200 g weight) were sham operated and treated subcutaneously with vehicle (Intact) or castrated and treated subcutaneously for 14 days with vehicle (ORX VEH), 3 mg/day SARM-1, SARM-2, an inactive SARM-3 or DHT. RNA from prostate was extracted, expression of 312 miRs was profiled and the miRs that are statistically different (P<0.05) from vehicle-treated castrate animals are expressed in the heatmap. ORX vehicle in the heatmap represents pooled data from vehicle and SARM-3 treated castrate animals. Values are expressed as an average with n = 5. The inset to the right of the heatmap represents the clustering of the individual animals. The numbers in brackets are animal numbers. The bar graphs are representative miR expressions selected from the heatmap. Values are expressed as average ± S.D. (n = 5). C. Ingenuity pathway analyses. The predicted targets of differentially expressed miRs were classified into major functional (left chart) and canonical (right chart) pathways using Ingenuity software. The bars represent pathways corresponding to the miR functional profiles of SARM-1, SARM-2 and DHT treated prostates in that respective order.