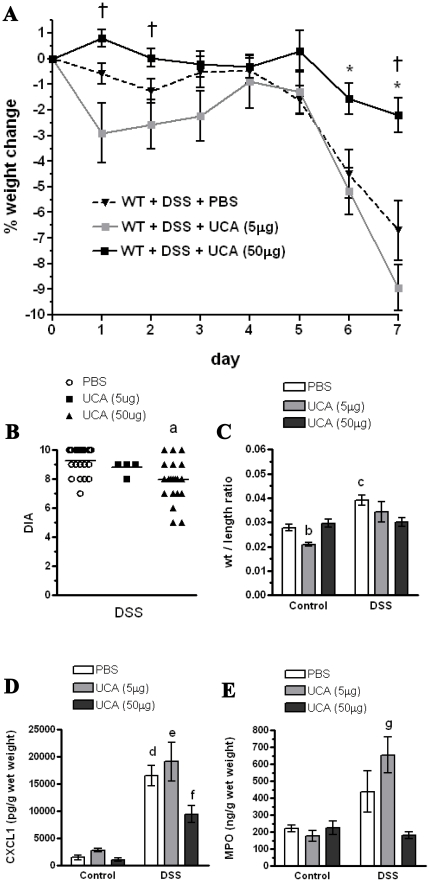
Figure 1. cis-UCA (50 µg) ameliorates dextran sodium sulfate (DSS)-induced disease in 129Sv/Ev mice.
129Sv/Ev mice were treated with 5% DSS for 7 days to induce acute colitis. Beginning on the first day of DSS administration mice were injected subcutaneously along the dorsal axis daily for 7 days with either 5 or 50 µg cis-UCA, or vehicle (PBS). Measurements were taken on Day 7. DSS treatment induced weight loss in mice, and this was attenuated by treatment with cis-UCA (50 µg). Mice receiving cis-UCA and DSS at the low dose (5 µg) had a transient increased weight loss compared with mice receiving the high dose of cis-UCA and DSS at days 1 and 2 (A). Total colonic disease activity score (DIA) was reduced by cis-UCA (50 µg) treatment (B). DSS treatment increased the colonic weight/length ratio, and this was prevented by treatment with cis-UCA (50 µg). Mice receiving the low dose of cis-UCA had a reduced weight/length ratio compared with PBS-treated and cis-UCA (50 µg) mice (C). DSS treatment increased levels of the chemokine, CXCL1, in colonic tissue, and this was attenuated by cis-UCA (50 µg) treatment (D). Total tissue levels of myeloperoxidase (MPO) were significantly increased in cis-UCA (5 µg) + DSS treated mice (E). n = 5–25 mice for all measurements. †: p<0.05 UCA (50 µg) compared with UCA (5 µg); *: p<0.05 UCA (50 µg) compared with PBS. a: p<0.01 UCA (50 µg) compared with PBS; b: p<0.01 Control UCA (5 µg) compared with control PBS, control UCA (50 µg), PBS+DSS, DSS+UCA (5 µg), and DSS+UCA (50 µg). c: p<0.05 PBS+DSS compared with control PBS, control UCA (5 µg), control UCA (50 µg), and DSS+UCA (50 µg). d: p<0.01 DSS+PBS compared with control PBS, control UCA (5 µg), control UCA (50 µg), and DSS+UCA (50 µg). e: p<0.01 DSS+UCA (5 µg) compared with control PBS, control UCA (5 µg), control UCA (50 µg), and DSS+UCA (50 µg). f: p<0.05 DSS+UCA(50 µg) compared with control PBS and control UCA (50 µg). g: p<0.05 DSS+UCA (5 µg) compared to control UCA (5 µg) and DSS+UCA (50 µg).