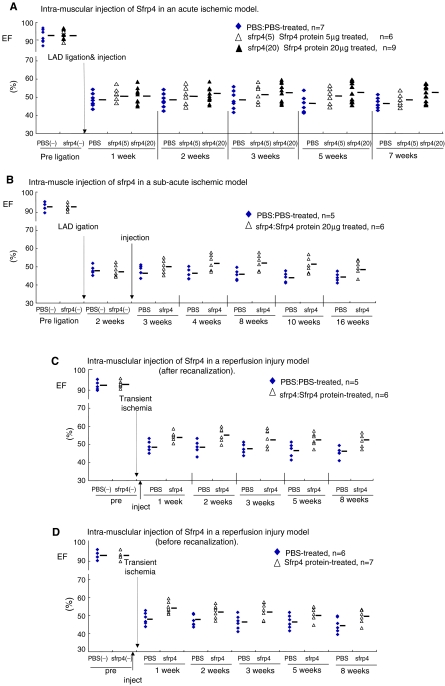
FIG. 2.
Sfrp4 recombinant protein exerts a cardio-protective effect. Cardiac function of PBS- or Sfrp4-treated rats as determined by EF before and after ischemic or recanalization injuries. EFs were monitored by echocardiography at the indicated time points and calculated as described in the Materials and Methods section. Other cardiac parameters, including fractional shortening (FS) and functional area change, are shown in Supplemental Table S4. (A) IM injection of Sfrp4 in an acute ischemic model. Ischemic hearts were generated by LAD ligation, and 100 μL of PBS (n = 7), 5 μg Sfrp4 protein (n = 6), or 20 μg Sfrp4 protein (n = 9) was injected to the ischemic border zones soon after LAD ligation. (B) IM injection of Sfrp4 in a subacute ischemic model. About 100 μL of PBS (n = 5) or 20 μg Sfrp4 protein (n = 6) was administered intramuscularly 2 weeks after LAD ligation. (C, D) IM injection of Sfrp4 just after (C) or before (D) recanalization injury. About 100 μL PBS or 20 μg Sfrp4 protein was administered intramuscularly after or before a transient 1 h LAD ligation. All treatments except 5 μg Sfrp4 (A) show either significant (p < 0.05) treatment or time-treatment interaction effects as judged by repeated measures ANOVA, and the effect of 20 μg Sfrp4 is different to that of 5 μg (p = 2.38E-4). Summary measurements are shown in Supplemental Fig. S1 and p-values are reported in Supplemental Table S3. PBS, phosphate-buffered saline; EF, ejection fraction; IM, intramuscular; ANOVA, analysis of variance. Color images available online at www.liebertonline.com/ten.