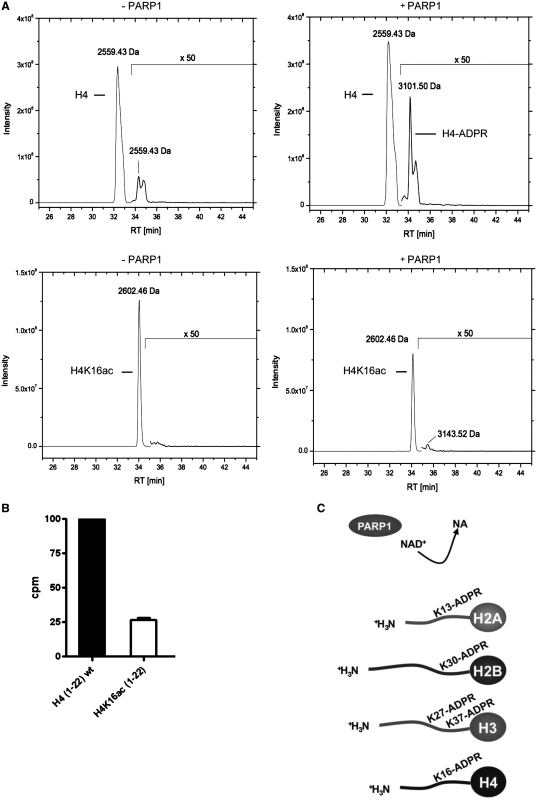
Figure 5.
ADP-ribosylation of the H4 peptide is impaired by H4K16 acetylation. (A) Elution profile of biotinylated H4 peptide (aa 1–22) and biotinylated H4K16ac peptide (aa 1–22) incubated with 100 μM NAD+ for 15 min without PARP1 (–PARP1) or in the presence of PARP1 (+PARP1) and subsequent ARH3 treatment. Acetone precipitated peptides were analyzed by LC–MS/MS using a C18 reversed-phase column and subsequent detection by mass spectrometry. (B) Histone H4 (aa 1–22) and acetylated H4K16ac (1–22) peptides were ADP-ribosylated with PARP1 for 15 min at 30°C with 100 nM 32P-NAD+. The peptides were purified by microvolume-C18 reversed phase columns, eluted into scintillation liquid and counted for incorporated 32P. Relative increase of counts per minutes was calculated over background (peptides added after termination of the reaction by 3AB). (C) Overview of the identified ADP-ribose acceptor sites within the amino-terminal core histone tails.