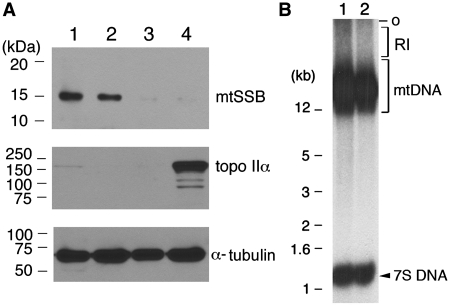
Figure 2.
An optimal reaction condition for 7S DNA synthesis in vitro. (A) Replication–competent CE (lane 1) was subjected to four consecutive centrifugations at 10 000g for 1 min. The clear supernatant (lane 3) obtained after the first centrifugation was stored, while the pellet (lane 2), enriched in mitochondria, was re-suspended in buffer G after four rounds of centrifugation. Subcellular fractions, including NE (lane 4), were analyzed by western blotting for the indicated protein with the following aliquots: lane 1, 15 µg of CE; lane 2, 4.2 µg of mitochondria fraction; lane 3, 15 µg of clear CE; lane 4, 10.8 µg of NE. (B) A duplicate set of replication reactions was performed in the standard mixture provided with replication–competent HeLa CE. After 2 h incubation, reaction mixtures were subjected to repeated centrifugations, as described in (A). After the final centrifugation, the pellets were treated with SDS (0.5%) and proteinase K (0.25 mg/ml) in a final volume of 12 µl. Following 30 min incubation at 37°C, the lysates were directly loaded on an agarose gel, and de novo synthesized DNAs were resolved by electrophoresis and visualized by autoradiography. O, the gel well. RI, replication intermediates.