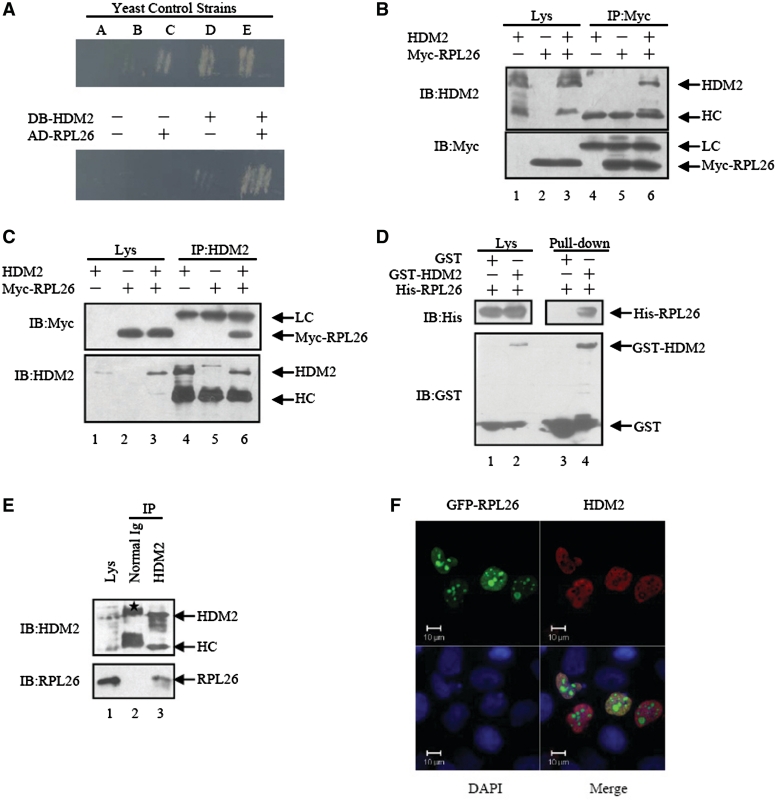
Figure 1.
RPL26 binds to HDM2. (A) HDM2 binds RPL26 in yeast two hybrid assays. A collection of yeast control strains, from A to E, have been developed that contain plasmid pairs expressing fusion proteins with a spectrum of interaction strengths from none, weak, moderately strong, strong to very strong. Transformants with indicated plasmids were cultured on SC-Trp-Leu-His-Ura plates and incubated at 30°C for 3–4 days. (B and C) Exogenous HDM2 and RPL26 interact with each other in HEK293 cells. HDM2 (3 μg), Myc-RPL26(3 μg) or both vectors (3 μg) were used for transfection. Whole-cell lysates were subjected to immunoprecipitation with anti-HDM2 or anti-Myc antibodies followed by immunoblotting with anti-Myc or anti-HDM2 antibodies. IP, immunoprecipitation; IB, immunoblotting; Lys, lysate; HC, heavy chain. LC, light chain. (D) Direct interaction between RPL26 and HDM2 revealed by GST pull-down assays. Both input and pull-down samples were subjected to immunoblotting with anti-His and anti-GST antibodies. (E) Binding between endogenous HDM2 and RPL26 in MCF7 cells. The lysates of MCF7 cells were immunoprecipitated with nonimmune mouse IgG or an antibody against HDM2. The immunoprecipitates were further separated by SDS–PAGE, and target proteins were detected with RPL26 and HDM2 antibodies. Ig, immunoglobulin. Asterisk indicates non-specific band. (F) HDM2 colocalized with RPL26 in the nucleoplasm. U2OS cells were transfected with GFP-RPL26 and HDM2. Scale bar, 10 μm.