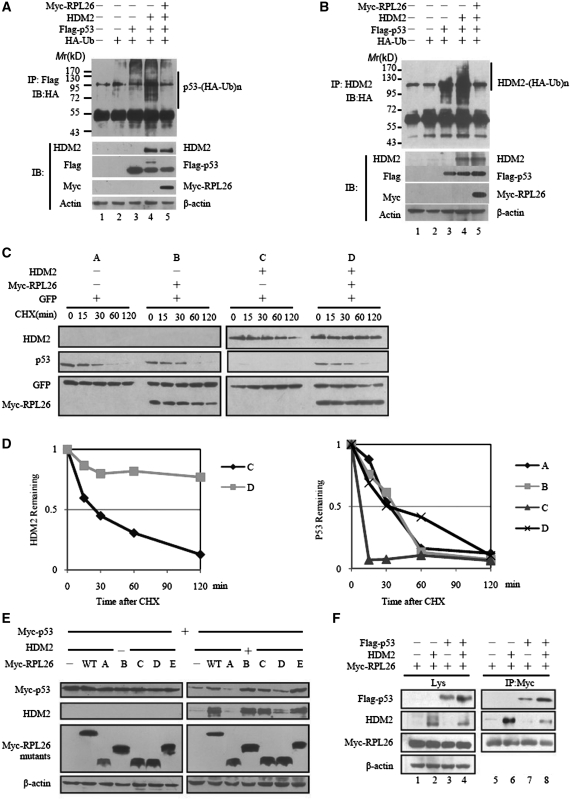
Figure 4.
RPL26 attenuates HDM2-mediated ubiquitination and degradation. (A and B) RPL26 inhibits HDM2-mediated p53 and HDM2 ubiquitination in H1299 cells. H1299 cells were transfected with combinations of RPL26 (2 μg)-, p53 (1 μg)- or HDM2 (2 μg)-encoding plasmids in the presence of the HA-ubiquitin (HA-Ub) (2 μg) plasmid as indicated. The cells were treated with MG132 (20 μM) for 8 h before harvesting. The cell extracts was immunoprecipited by Flag antibody (A) or HDM2 antibody (B). Ubiquitinated proteins were detected by immunoblotting with the anti-HA antibodies. Ubiquitinated p53s [p53-(HA-Ub)n] (A) or Ubiquitinated HDM2s [HDM2-(HA-Ub)n] (B) is indicated to the upper panels. The expression levels of HDM2, p53 and L26 are shown in the lower panels. (C) Half-life analysis of p53 and HDM2 in the presence or absence of overexpressed RPL26. U2OS cells were transfected with 0.2 μg of Myc-RPL26 in the presence of GFP (50 ng) with (−) or without (+) HDM2 (0.4 μg) as indicated. After 24 h transfection, cells were exposed to the protein synthesis inhibitor CHX (100 μg/ml) for different times. Target proteins were detected by immunoblotting. (D) Plot of the p53 and HDM2-expression levels following CHX treatment. The value is normalized to the levels of GFP. (E) RPL26 modulates p53 by interacting with HDM2. Wild-type and mutant RPL26 were overexpressed in MEF (p53−/−/mdm2−/−) cells with or without HDM2 in the presence of p53, and the target proteins in whole-cell lysates were detected by immunoblotting. (F) RPL26 modulates the HDM2–p53 interaction by forming a ternary complex among RPL26, HDM2 and p53. HEK293 cells were transfected with combinations of plasmids as indicated. Cell lysates were immunoprecipitated by Myc antibody followed by immunoblotting with Myc, Flag-HRP, HDM2 and β-actin antibodies for the immunoprecipitates or the whole-cell lysates.