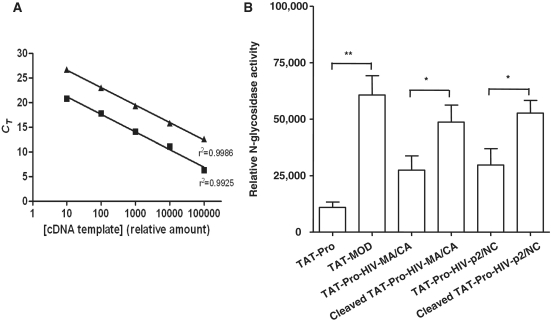
Figure 3.
In vivo N-glycosidase activity of TAT-fused maize RIP and variants in mouse macrophage 28S rRNA (J774A.1). During first-strand cDNA synthesis, reverse transcriptase preferentially inserts an adenine at the site of depurination, resulting in a T to A transversion in sequencing reads. N-glycosidase activity was determined by qPCR using primers that target the modified site. (A) qRT-PCR efficiency test for primer pairs. Signals were obtained from the amplification of serially diluted cDNA synthesized from the RNA of TAT-MOD treated cells. Filled square indicates total 28S rRNA and filled triangle indicates depurinated rRNA. The relative amount of cDNA template was plotted against the corresponding threshold cycle number in log scale and fitted with a linear regression model. SEMs were less than 1% of the corresponding CT values. (B) Relative N-glycosidase activity of the TAT-fused maize RIP and variants. The relative N-glycosidase activity was calculated as the relative amount of altered rRNA of sample-treated cells over the untreated cells and mean ± SEM was calculated for the graphic presentation. Unpaired t-test was performed for statistical analysis (n = 6) (*P < 0.05, **P < 0.01).