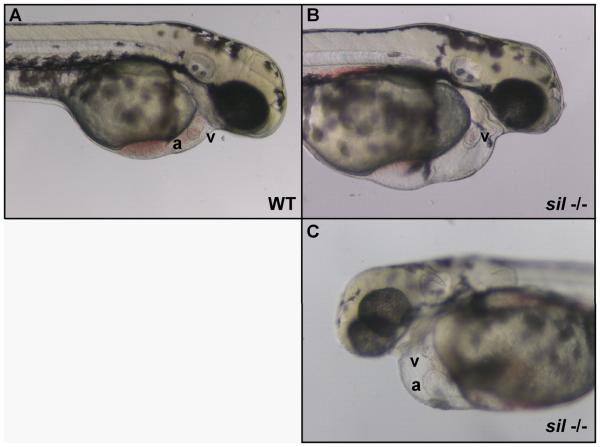
Figure 1. Characterization of the sil phenotype.
Lateral view of wild-type (WT) (A) and silm656 mutant (−/−) (B, C) embryos at 2 dpf. The ventricle (v) of the sil mutant embryo (B, C) is visibly compacted and misshapen compared to wild-type (A), while the atrium (a) of the sil mutant (C) has become enlarged. The silm656 mutant embryo (B, C) also exhibits pericardial edema and has reduced circulation as compared to wild-type (A). Mutant embryos homozygous for the silsk25 allele exhibit the same phenotype.