Fig. 5.
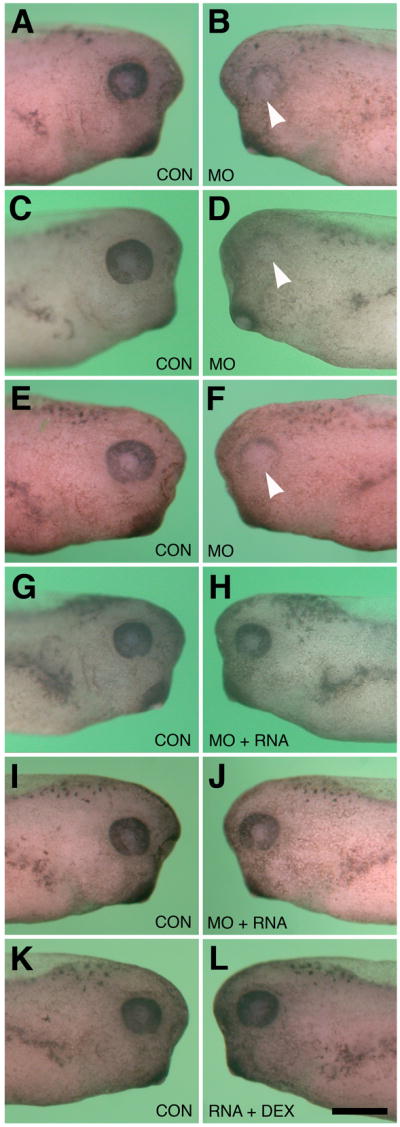
Effects of GPR84 Morpholino-mediated knockdown and RNA rescue on eye development. Dorsal is toward the top in each figure. A–F: Typical eye defects following unilateral injection of lissamine-tagged H127MO into single blastomeres at the two-cell stage. All larvae shown are stages 37–39. A: Normal uninjected (CON) side. B: Corresponding H127MO injected side (5.24ng) to that shown in A. Minor eye defect is observed on this side, as indicated by arrowhead. C: Normal uninjected side. D: Corresponding H127MO injected side (6.5ng) to that shown in C. Severe eye defect is observed on this side, as indicated by arrowhead. E. Normal uninjected side. F: Corresponding H127MO injected side (10.74ng) to that shown in E. Severe eye defect is observed on this side, as indicated by arrowhead. G. Normal uninjected side. H: Corresponding injected side to that shown in G. Representative normal eye development follows co-injection of H127MO (6.5ng/blastomere at the two-cell stage) and 800pg synthetic altGPR84 mRNA. I. Normal uninjected side. J. Corresponding injected side to that shown in I. Typical normal morphological development following co-injection of H127MO (6.5ng/blastomere at the two-cell stage) and 1200pg synthetic altGPR84 mRNA. K. Normal uninjected side. L. Normal eye development following injection of 1200pg synthetic altGPR84 RNA diluted with fluorescent dextran. The scale bar in L is equal to 400 μm.
