Figure 1.
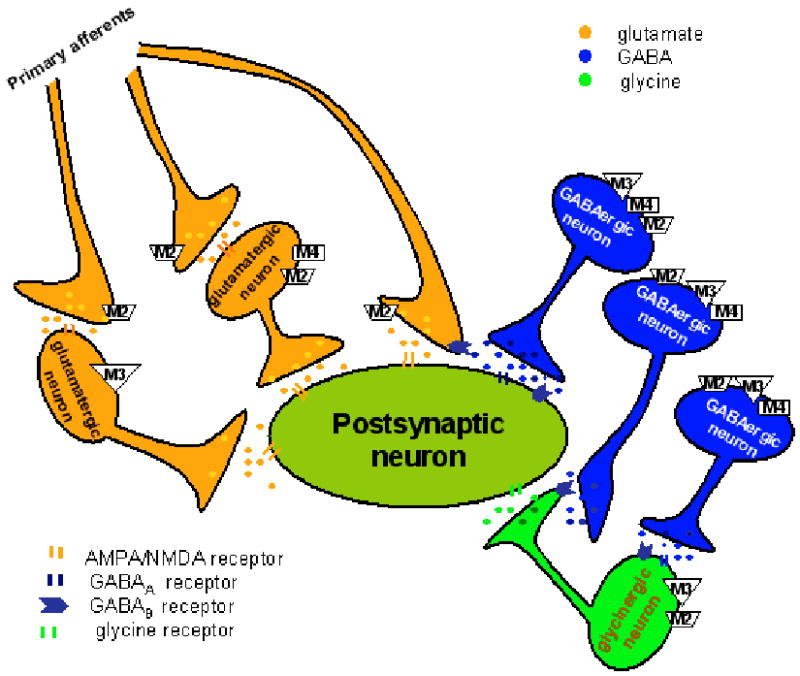
Schematic depicting the distribution and interaction between primary afferent terminals and interneurons in the rat spinal dorsal horn upon stimulation of the three mAChR subtypes. Activation of the M2 subtype on the primary afferent terminals and M3 and M2/M4 subtypes on a subpopulation of interneurons inhibit glutamatergic input to dorsal horn neurons. Stimulation of M2, M3, and M4 subtypes on the somatodendritic site of GABAergic interneurons can potentiate synaptic GABA release. Furthermore, the M2 and M3 subtypes present on the somatodendritic site of glycinergic interneurons are responsible for increased glycinergic input to spinal dorsal horn neurons upon activation of mAChRs. Additionally, concurrent stimulation of mAChRs on adjacent GABAergic interneurons can attenuate glycinergic and glutamatergic input to spinal dorsal horn neurons through GABA spillover and activation of presynaptic GABAB receptors.
