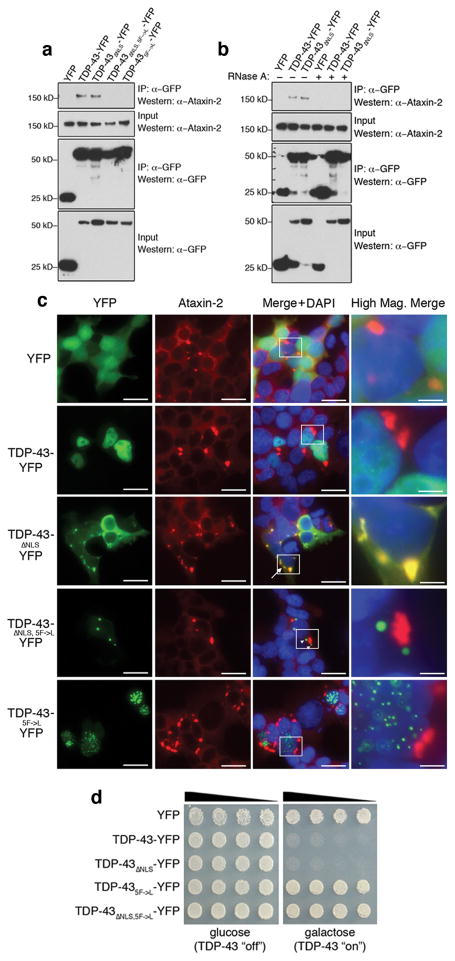
Figure 3.
Ataxin-2 and TDP-43 interact in a manner dependent on RNA. a) TDP-43 and Ataxin-2 associate in mammalian cells in a manner dependent on the RRMs. HEK293T cells were transfected with plasmids encoding YFP, TDP-43-YFP, TDP-43 ΔNLS-YFP (NLS mutant localizes to cytoplasm), TDP-43 ΔNLS,5F→L-YFP (NLS mutant + RNA-binding mutant), or TDP-435F→L-YFP (RNA-binding mutant). Protein was immunoprecipitated with anti-GFP antibody, and then subjected to immunoblotting with anti-Ataxin-2 to detect endogenous Ataxin-2. Whereas TDP-43 and TDP-43 ΔNLS both interact with Ataxin-2, RNA-binding mutant versions do not. b) Co-IP in HEK293T cells as in (a), but now with lysates treated with RNase. The interaction between Ataxin-2 and TDP-43 seen normally was abolished upon RNase treatment. c) HEK293T cells transfected with YFP-tagged WT and mutant TDP-43 constructs then immunostained for endogenous Ataxin-2. Normally, Ataxin-2 is localized to the cytoplasm forming occasional cytoplasmic accumulations. TDP-43 localized to the nucleus in a diffuse pattern. TDP-43 ΔNLS localized to the cytoplasm where it occasionally formed cytoplasmic aggregates; these aggregates always co-localized with Ataxin-2 cytoplasmic accumulations (arrow). Abolishing the ability of TDP-43 to interact with RNA (TDP-43 ΔNLS, 5F→L or TDP-435F→L) eliminated Ataxin-2 colocalization (arrowheads). TDP-435F→L-YFP was restricted to the nucleus where it formed multiple foci. Scale bar is 2.5 μm for merge panels and 0.5 μm for high mag. merge panels. d) Yeast spotting assays for TDP-43 toxicity. Whereas WT and TDP-43 ΔNLS constructs are toxic, mutations of TDP-43 that prevent RNA binding abolish toxicity.