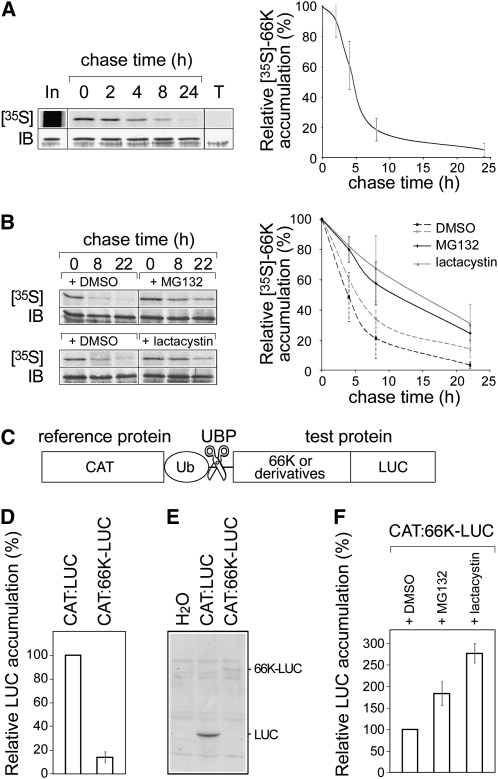
Figure 2.
Degradation of 66K Is Mediated by the UPS.
(A) Pulse-chase experiments: Arabidopsis transgenic cells expressing 66K-His were pulse labeled with [35S]Met and [35S]Cys and then chased for the times indicated. The left panel shows a representative experiment. Cell lysates were subjected to immunoprecipitation with anti-66K antibody, and the resulting precipitates were subjected to SDS-PAGE and phosphor imaging ([35S]; top). In, input protein recovered immediately after the labeling period; T, control experiment performed using non transformed cells. The band intensities were quantified, corrected for the total amount of 66K present in the sample as determined by immunoblotting (IB; bottom), and expressed as a percentage of the corresponding value at the beginning of the chase period. The right panel shows the data as mean ± sd of n = 5 replicates.
(B) Pulse-chase experiments as in (A) were performed in the presence of DMSO, MG132 (n = 4), or clastolactacystin β-lactone (n = 2).
(C) Schematic representation of the chimeric protein used in the UPR assay. Reference and test proteins are separated by a ubiquitin moiety (UbK48R) that is cleaved by cellular ubiquitin-specific processing proteases (UBP).
(D) Stability of LUC fusion proteins as measured using the UPR assay. LUC activity was determined and divided by the activity of the CAT internal control. The results are shown as percentages of the control. Data are mean ± sd of n = 14 replicates.
(E) Protein extracts from cells transfected with pΩ-CAT:LUC or pΩ-CAT:LUC-66K were immunodetected using anti-LUC antibody. Samples were adjusted to equal CAT activity and equal total protein by addition of negative control (water) extract to samples with lower protein content.
(F) Stability of LUC fusion proteins was measured using the UPR assay in the presence of DMSO, MG132 (n = 8), or clastolactacystin β-lactone (n = 6).