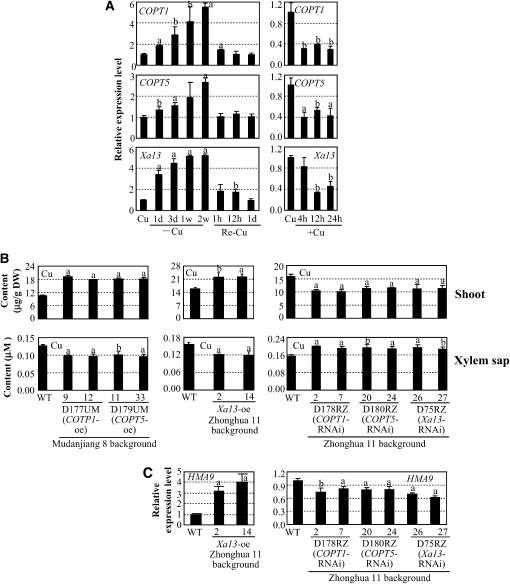
Figure 4.
Xa13, COPT1, and COPT5 in Cu Transport in Rice.
Gene expression was analyzed by qRT-PCR. Each data point represents mean (three replicates) ± sd; the “a” or “b” indicates a significant difference was detected between a treatment or a transgenic line and the control or wild-type plants at P < 0.01 or P < 0.05 level, respectively.
(A) Expression of Xa13, COPT1, and COPT5 in shoot is influenced by Cu levels. Rice variety Zhonghua 11 at the four-leaf stage grown in hydroponic culture was used for qRT-PCR analysis. Cu, standard physiologic Cu (0.2 μM); –Cu, Cu deficiency; Re-Cu, retransferring plants to normal culture (containing 0.2 μM Cu); +Cu, 50 μM Cu.
(B) Modulating COPT1, COPT5, and Xa13 expression influenced Cu accumulation in shoots and xylem sap in rice at booting stage. Xa13-suppressing plants were in T0 generation, and other transgenic plants were in T2 generation. DW, dry weight; oe, overexpression, RNAi, RNA interference (suppression).
(C) Modulating COPT1, COPT5, and Xa13 expression influenced the expression of HMA9. The samples were from the same plants described in (B).