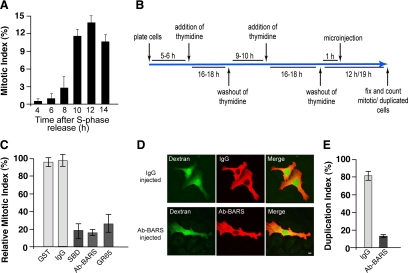
Figure 1.
Inhibition of Golgi fragmentation causes a block of cell cycle progression in HeLa cells. (A) Quantification of the mitotic index of cells grown on coverslips and arrested in S phase using the double-thymidine block, as shown schematically in B. The cells were fixed at the indicated times after the S phase block release, the DNA was labeled with Hoechst-33342, and the mitotic indices were calculated under fluorescence microscopy (see Materials and Methods). (C) Quantification of cells treated as illustrated in B. One hour after the S phase block release, the cells were microinjected with fluorescent dextran as injection marker, together with recombinant GST (8 mg/ml), generic IgGs (5 mg/ml), recombinant SBD (8–12 mg/ml), an anti-BARS antibody (Ab-BARS; 5–7 mg/ml), or recombinant GRASP65 (GR65; 8–10 mg/ml). The cells were fixed at the mitotic peak (12 h after S phase release) and processed for immunofluorescence under confocal microscopy, with DRAQ5 (blue) for the cell cycle phase. The relative mitotic indices were calculated as percentages of microinjected cells in mitosis normalized to nonmicroinjected cells on the same coverslip. (D and E) HeLa cells were treated as described in C with microinjections with generic IgGs (5 mg/ml) and the anti-BARS antibody (Ab-BARS; 5–7 mg/ml). The cells were fixed 19 h after the S phase block release and processed for immunofluorescence under confocal microscopy, with fluorescently labeled secondary antibodies to reveal IgG- or anti-BARS-injected cells. (D) Representative images of post-mitotic couplets (top) and premitotic singlets (bottom), microinjected as indicated. Bar, 10 μm. (E) Quantification of duplication index as percentages of postmitotic couplets (see Materials and Methods). Quantification data are means ± SD from two (A and E) and four (C) independent experiments, each carried out in duplicate. More than 200 cells were microinjected for each condition.