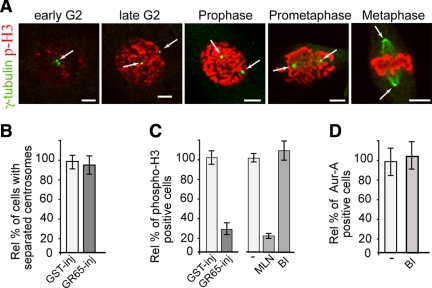
Figure 6.
Block of Golgi fragmentation does not require Plk1 to inhibit Aur-A recruitment. Cells were grown on coverslips and arrested in S phase using the double-thymidine block and processed for immunofluorescence under confocal microscopy. (A) Representative images of cells at the indicated cell cycle stages, labeled with an antibody against γ-tubulin (green, arrow) and with DRAQ5 (data not shown) for cell cycle phase, and labeled with antibodies against phosphorylated histone H3 (p-H3, red). (B and C) The cells were either nonmicroinjected or microinjected 1 h after thymidine washout with recombinant GST (GST-inj, 8 mg/ml), or recombinant GRASP65 (GR65-inj, 8–10 mg/ml), and with FITC-conjugated dextran as microinjection marker. For the noninjected cells, 8 h after thymidine washout they were treated with vehicle (−) or 0.25 μM MLN8054 (MLN), or with 100 nM BI2536 (BI). The cells were then processed 12 h after thymidine washout, for immunofluorescence under confocal microscopy with antibodies against γ-tubulin (B) or phosphorylated histone H3 (C). The relative percentages of cells with separated centrosomes (B) or positive for phosphorylated histone H3 (C) were calculated according to the relevant nonmicroinjected cells on the same coverslip or to cells treated with vehicle (−). (D) Eight hours after S phase block release, the cells were either left in growth medium (−) or treated with 100 nM BI2536 (BI), fixed at the mitotic peak (at 12 h) and labeled with antibodies against T288-phosphorylated Aur-A. The relative percentages of PT288 Aur-A–positive cells were calculated according to the cells treated with dilution buffer (−). Quantification data are means ± SD from at least two independent experiments, each carried out in duplicate. More than 200 cells were microinjected for each condition. Bar, 5 μm.