Figure 1.
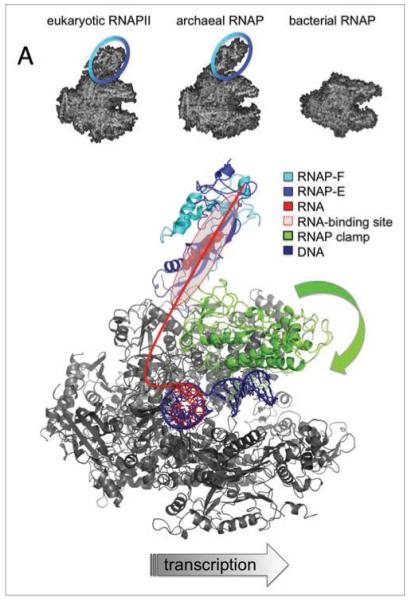
Interactions between RNAP subunits F/E and the transcript RNA modulate transcription elongation and termination. (A) shows the structures of RNAPs in Eukarya (pdb 1NT9), Archaea (pdb 2PMZ) and Bacteria (pdb 1I6V). RNAP subunits F/E form a stalk-like protrusion, which is a signature module of eukaryotic and archaeal RNAPs (highlighted with blue circle). A model of the archaeal transcription elongation complex in top view (S. shibatae RNAP pdb 2WAQ and DNA/RNA scaffold pdb 1Y1W). RNAP subunits, motifs and nucleic acids are colored according to the key in the figure. The path of the RNA transcript is sketched as a red line, and the residues in subunit E that mediate the RNA binding are highlighted as red spheres.12 The closure of the flexible RNAP clamp over the DNA binding channel is indicated with a green block arrow.
