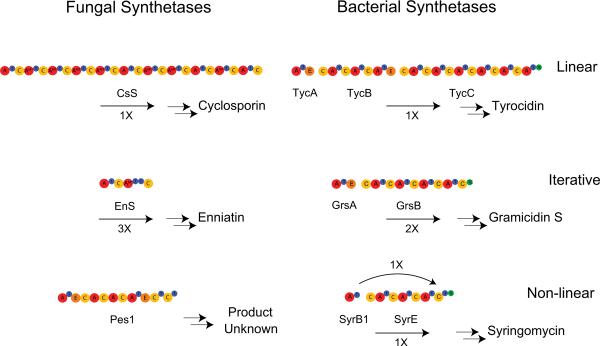
Fig. 5.
Overview of fungal vs. bacterial NRPSs. NRPSs can be divided into three types, linear (a), iterative (b) and non-linear (c). Fungal NRPSs generally follow a single megasynthetase logic, whereas bacterial NRPS pathways are generally spread over a greater number of polypeptides. Fungal NRPSs are also rich in A-MT domains, a feature rarely seen in bacterial NRPSs. CsS: cyclosporine synthetase; EnS: enniatin synthetase; Pes1: synthetase encoded by pes1, TycA, B, C: tyrocidine synthetase A, B, C; GrsA, B: gramicidin S synthetase A, B; SyrB1, E: syringomycin synthetase B1, F.