Fig. 1.
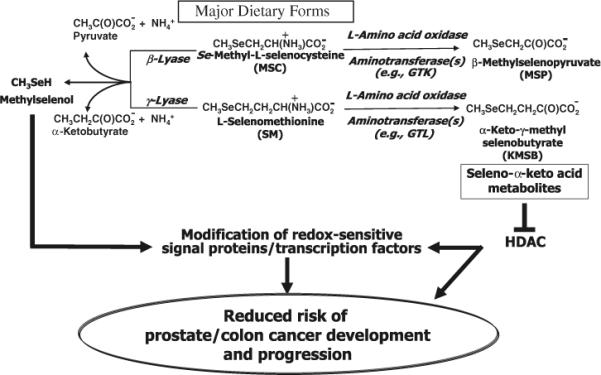
Proposed metabolic pathways for naturally occurring organoselenium compounds. Dietary seleno amino acids can undergo either β-/γ-elimination reactions with formation of CH3SeH or transamination/oxidative deamination reactions with formation of seleno α-keto acids. CH3SeH from the former reaction is a putative anticancer metabolite of organoselenium compounds which can react with redox sensitive signal proteins. The α-keto acid metabolites from the latter reaction exhibit HDAC inhibitory properties in human prostate and colon cancer cells which is symbolized by ⊥
