Figure 1.
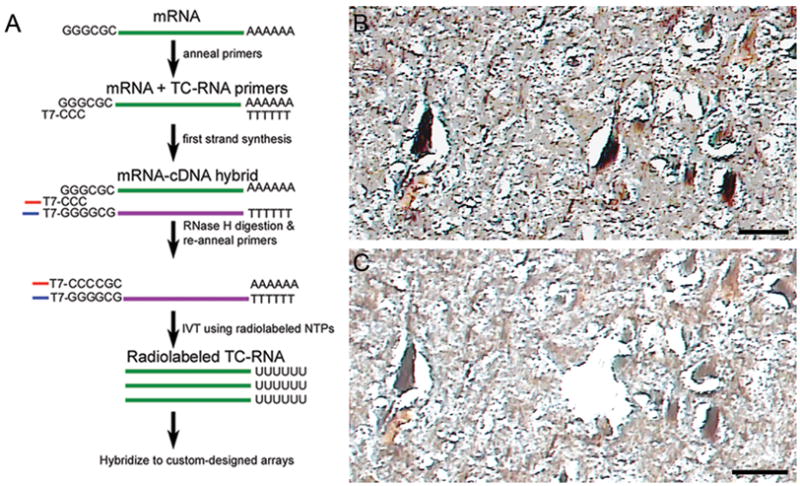
TC RNA amplification procedure and LCM of CA1 hippocampal neurons.
A. Schematic overview of the TC RNA amplification procedure. mRNA extracted from LCM captured cells (green line) and the TC primer serve as templates for the first strand synthesis with poly d(T) acting as a primer. First strand cDNA consists of three portions, the 5′ end comprised of the poly d(T), the mRNA complementary portion in the middle (purple line), and the 3′ end is comprised of the TC primer complementary to the cDNA (denoted as TC′). The TC′ portion hybridizes with the TC primer present in the reaction and forms a double stranded region which provides a functional RNA synthesis promoter for in vitro transcription and robust RNA amplification.
B. Neurofilament-immunoreactive CA1 neurons in the hippocampal pyramidal cell layer from a subject with AD prior to LCM. Tissue sections were dehydrated but not coverslipped to enable proper execution of the LCM process. Scale bar: 50 mm.
C. Slightly larger image in B following LCM of an individual CA1 neuron. Scale bar: 50 mm.
