Figure 2.
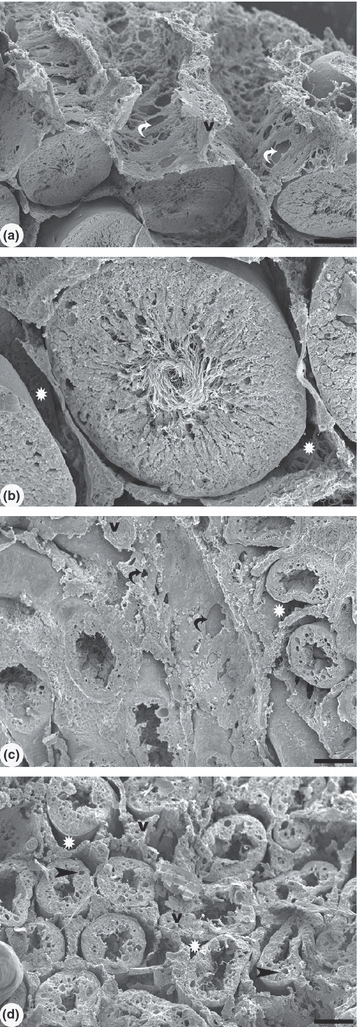
Scanning electron microscopy of control rat testis and under the effect of cadmium after 56 days. (a) Testicular parenchyma shows a delicate lattice with large fenestrae of interstitial tissue. The seminiferous tubules are well preserved in the control group. A large space for fluid was observed between the interstitial tissue and the seminiferous tubules. (b) Detail of the seminiferous tubule with intact epithelium and the presence of spermatozoa in the lumen. (c) In cadmium (1.2 mg/kg BW) treated group, the interstitium shows a dense fibrous aspect with few fenestrae and reduced fluid space (white star). (d) The reduced epithelium height and vacuolization is observed in the seminiferous tubules. Note the absence of spermatozoa in the lumen. The fluid space was diminished or not clearly observed. Blood vessels (v) have thicker walls. White and black curved arrows: fenestrae. Scale bars: a, c, d: 100 μm; b: 10 μm.
