Figure 4.
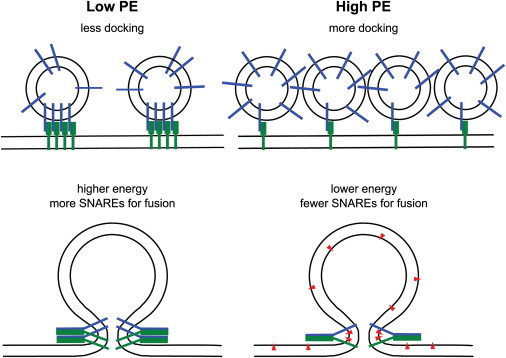
Models explaining the effects of PE on docking and fusion. In the absence of PE, we hypothesize that SNAREs may be more clustered in cholesterol-containing target and vesicle membranes leading to fewer docking sites. The membrane-bending energy in the absence of PE is higher requiring more SNAREs for fusion. In the presence of PE, SNARE clusters may be (partially) dispersed leading to more docking sites. The inverted cone shape of PE (red triangles) facilitates curved intermediate membrane structures (including hemifusion stalk, not shown) and thus lowers the energy of fusion intermediates requiring fewer SNAREs for fusion.
