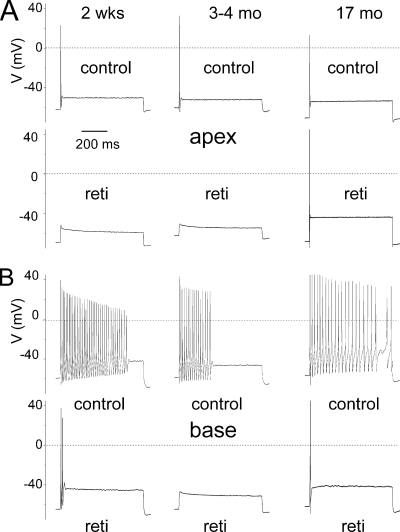
FIGURE 5.
Retigabine, a Kv7-mediated current agonist, attenuated the excitability of SGNs from the apical and basal turn of the cochlea. A, action potentials were recorded from SGNs isolated from the apical turn of the cochlea by current injection of 0.1 nA. Shown are representative profiles recorded from 2-week-old (left panel) and 3–4- and 17-month-old SGNs. B, using similar recordings from basal SGNs, control neurons responded to current (0.2 nA) injected with repetitive firing that showed adaptation. Retigabine (reti) (10 μm) attenuated the AP firing. The number of spikes elicited and Vrest in apical cells for control were 1 ± 0 and −66 ± 4 mV and after application of retigabine were 0 ± 0 (n = 9) and −75 ± 5 mV, respectively. The number of spikes elicited and Vrest in basal cells for control were 29 ± 12 and −59 ± 3 mV and after application of retigabine were 1.5 ± 0.7 (n = 9) and −66 ± 3 mV, respectively.