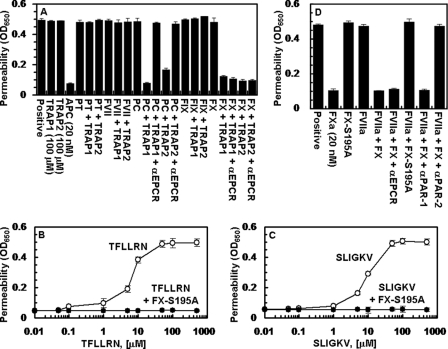
FIGURE 1.
Effect of receptor occupancy by vitamin K-dependent coagulation protease zymogens on PAR-1- and PAR-2-dependent cellular responses. A, EA.hy926 cells were pretreated for 30 min with buffer control or near physiological concentrations of protein C (PC, 80 nm), prothrombin (PT, 1.39 μm), FVII (10 nm), FIX (90 nm), and FX (175 nm) in the absence and presence of receptor agonist peptides specific for either PAR-1 (TFLLRN) or PAR-2 (SLIGKV) (100 μm, 3 h) before inducing the permeability with thrombin (5 nm for 10 min). When function-blocking anti-EPCR antibody (αEPCR, 25 μg/ml) was present, cells were incubated with the antibody for 30 min before pre-treatment with zymogens. APC (20 nm) was used as a control for its known cytoprotective activity. B, the concentration dependence of activation of endothelial cells by the PAR-1 agonist peptide (TFLLRN, 3 h) before (○) or after (●) treatment with FX-S195A (50 nm for 30 min). C, the same as B except that the PAR-2 agonist peptide (SLIGKV) was used for activation. D, the same as A except that the TF-transfected endothelial cells were pretreated with buffer control (positive) or with the indicated proteins (FXa, 20 nm; FX-S195A, 50 nm; FVIIa, 10 pm; FX, 175 nm) before inducing permeability with thrombin (5 nm, 10 min). In the presence of function-blocking anti-PAR-1 and anti-PAR-2 antibodies (25 μg/ml), cells were first preincubated with antibodies for 30 min. All results are means ± S.D. of three different experiments.