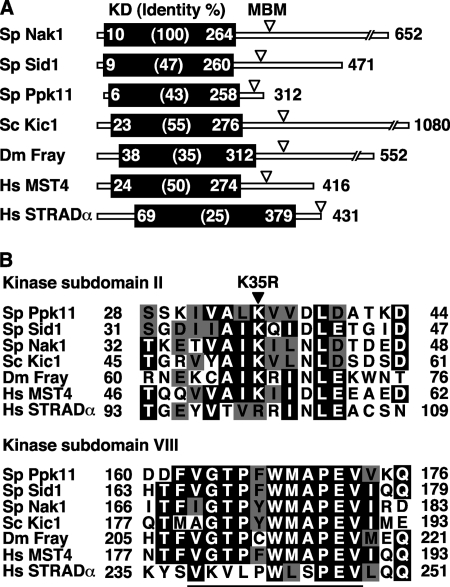
FIGURE 1.
Structure of GCKs. A, identity of KD and MBM of GCKs. S. pombe Nak1, Sid1, and Ppk11, S. cerevisiae Kic1, Drosophila melanogaster Fray, and Homo sapiens MST4 and STRADα are shown. The identities (%) between Nak1 and other GCKs and the amino acid number of the beginning and the end of the KD are indicated. Arrowheads indicate the position of the putative MBM. B, alignment of the kinase subdomain of GCKs. Identical or similar residues are represented in black or gray, respectively. The kinase domain is subdivided into 11 conserved subdomains, and subdomain II is essential for the kinase activity by acting as the ATP binding site. The solid arrowhead indicates the conserved lysine that was mutated to arginine to construct the Ppk11 kinase dead mutant (ppk11-K35R). In subdomain VIII of Ste20 group kinases, there is a distinct peptide sequence, (v/i)GTPyWMAPEv (a small letter indicates less conservation), termed the Ste20 signature sequence. This sequence is underlined. The sequences were aligned by using the software ClustalW provided by PBIL (Pole Bio-Informatique Lyonnais).