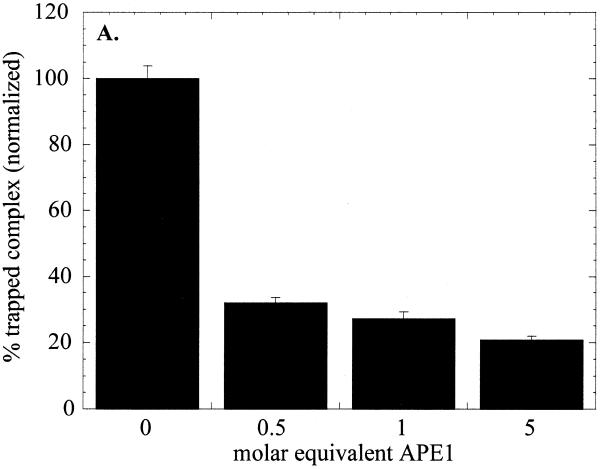
Figure 6.
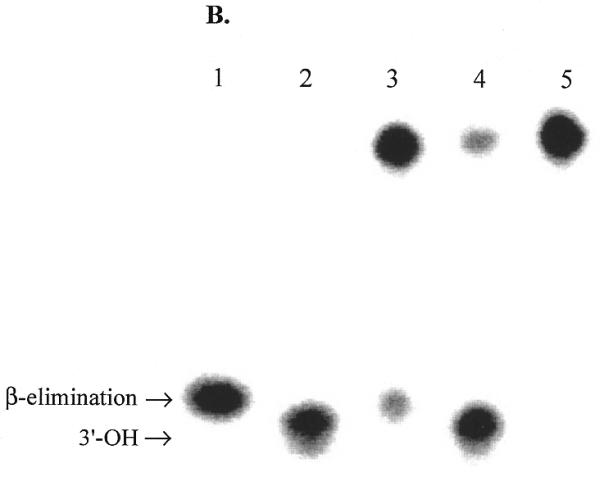
Effect of APE1 on sodium borohydride trapping and AP lyase activity of OGG1. OGG1 (5 nM) was incubated with 1 nM 8-oxoG·C-containing oligo substrate in the presence of 1 mM sodium borohydride with varying amounts of APE1 (2.5–25 nM) for 30 min at 37°C. (A) After termination of the reaction by adding 10 µl of 2× SDS sample buffer and heating for 5 min at 100°C, the trapped complexes were separated from free substrate by SDS–PAGE. (B) Analysis of 3′-termini generated by OGG1 and APE1. Lanes 1 and 2, mobility markers for the 3′-termini characteristic of the β-elimination product and AP site, respectively. Lane 1, 1 nM 5′-labeled U·C-containing duplex oligo was incubated at 37°C for 5 min with 1 µg E.coli Udg and 1 µg Nth; lane 2, 1 nM 5′-labeled U·C oligo was incubated with 1 µg E.coli Udg and 1.25 µM APE1; lanes 3–5, 1 nM 5′-labeled 8-oxoG·C-containing oligo was incubated for 5 min at 37°C with 30 nM OGG1 (lane 3), 10 nM OGG1 and 50 nM APE1 (lane 4) or 10 nM OGG1 and 500 nM APE1 (lane 5). An aliquot of 1 mM MgCl2 was present in lanes 1–4 and 1 mM EDTA in lane 5. All reactions were terminated with SDS (0.5%) and glycerol (5%) without heating.