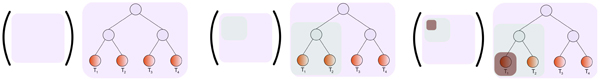
Figure 1.
Example of a hierarchical decomposition. According to a simple binary tree, it is shown how each node defines a subset of tasks (a block in the corresponding kernel matrix on the left). Here, the decomposition is shown for only one path: The subset defined by the root node contains all tasks, the subset defined by the left inner node contains t1 and t2 and the subset defined by the leftmost leaf only contains t1. Accordingly, each of the remaining nodes defines a subset Si that contains all descendant tasks.