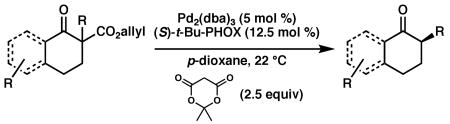
Table 3. Enantioconvergent Decarboxylative Protonationsa.
 | |||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| entry | substrate | product | ee A (%) | time (h) | yield (%) | ee B (%) | |
| 1 | 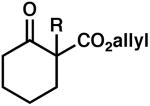 |
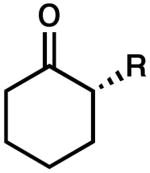 |
R = Me | 88 | 0.5 | 99b | 86 (R) |
| 2 | R = Et | 92 | 0.5 | 99b | 89 (R) | ||
| 3 | R = Bn | 83 | 0.5 | 90 | 78 (S) | ||
| 4 | 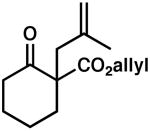 |
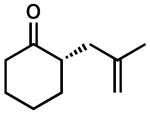 |
91 | 5 | 87 | 89 | |
| 5 | 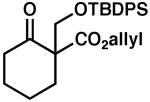 |
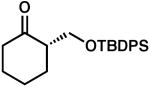 |
85 | 0.5 | 97 | 80 | |
| 6 | 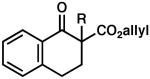 |
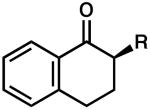 |
R = Me | 90 | 0.5 | 86 | 77 (S) |
| 7 | R = Allyl | 82 | 0.5 | 83 | 77 (R) | ||
| 8 | 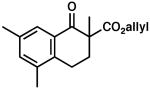 |
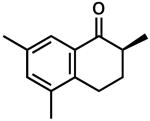 |
– | 0.5 | 77 | 77 | |
| 9 | 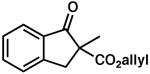 |
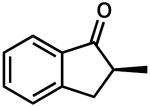 |
– | 0.5 | 79 | 61 (S) | |
Reactions were performed on two different scales, A: 0.1 mmol of substrate, and B: 0.3 mmol of substrate, each at 0.033 M in p-dioxane. Column ee A reflects results for conditions A; time, isolated yield, and ee B are reported for conditions B. Isolated yields from conditions A were comparable to those with conditions B. The major enantiomer was the same under either set of conditions. Enantiomeric excess was measured following chromatography on silica gel; no erosion of ee was observed as a result of purification.
GC yield using tridecane as internal standard.
