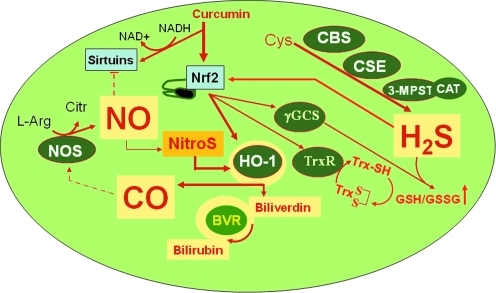
FIG. 6.
Endogenous biosynthetic pathways of (a) NO, involving NOSs, (b) CO, involving HO isoforms (HO-1, HO-2), and (c) H2S, involving CBS, CSE, and MPST. Methionine, which is derived from alimentary sources, is converted to S-adenosylmethionine by methionine adenosyltransferase. S-adenosylmethionine is subsequently hydrolyzed to homocysteine by glycine N-methyltransferase. Cystathionine β-synthase catalyses the production of cystathionine by transferring serine to homocysteine. Cystathionine γ-lyase, a pyridoxal 5′-phosphate-dependent enzyme, subsequently converts cystathionine to cysteine. In the mitochondria, cysteine can get converted to 3-mercaptopyruvate by aspartate aminotransferase, which can then be converted to H2S by MPST. CBS, cystathionine β-synthase; CO, carbon monoxide; CSE, cystathionine γ-lyase; HO, Heme oxygenase; H2S, hydrogen sulfide; MPST, 3-mercaptopyruvate sulfur transferase; NO, nitric oxide; NOS, NO synthase.