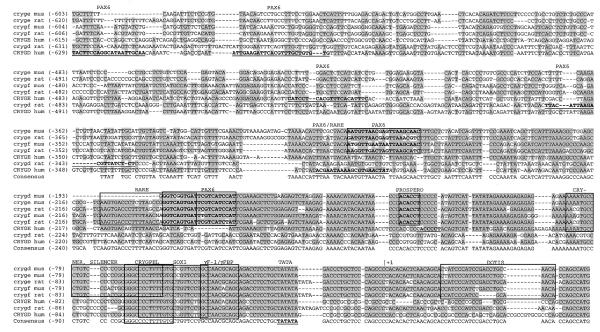
Figure 1.
The Crygd/e/f promoters of mammals. The mouse, rat and human Crygd/e/f promoters were compared by AlignX. Identical stretches are underlined in grey. The mouse and rat Crygd/e/f promoters are highly conserved between position –230 (of the mouse Crygf sequence) and the translational start site. It is commonly accepted that these sequences are necessary for lens-specific expression. The following sequence elements can be observed in all of them (positions refer to the mouse Crygf sequence): RARE, retinoic acid response element, –208/–183 (9,10); CRYNER, γ-crystallin nested repeats, –87/–59 (11); SILENCER, –76/–58 (12,13); CRYGPEL, common γ-crystallin promoter element, –67/–54 (14); SOX1, Sox1-binding site, –63/–44 (15); γF-1/γFBP, γF-crystallin binding protein, 46/–36 (16–18); TATA box, –23/–18; DOTIS, downstream of transcription initiation site, +15/+35 (19,20). Novel putative binding sites for Pax6 and Prospero predicted by MatInspector Professional are boxed in bold. The GenBank/EMBL accession nos of the aligned sequences are: mouse Crygf, M11039 (21); rat Crygf, M19357 (22); mouse Crygd, M16512 (23); mouse Cryge, X57855 (40); rat Cryge, M19359 (22); human CRYGF, K03009 (24); human CRYGD, K03005 (24); rat Crygd, M19359 (22), human CRYGE, K03007 (24); human CRYGD and ψCRYGE, AC018961 (25).