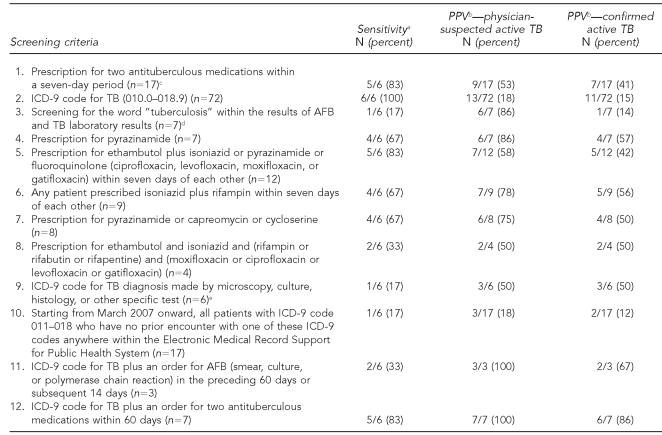
Table 1.
Candidate algorithms assessed for sensitivity and PPV for TB in a derivation cohort of electronic medical record data from Harvard Vanguard Medical Associates, June 2006 through July 2007
aReported relative to the total number of patients with confirmed active TB diagnosed or treated at a Harvard Vanguard Medical Associates facility.
bReported relative to the total number of patients captured by each individual algorithm. All captured cases of active TB were included when calculating PPV, including known patients diagnosed and treated at non-Harvard Vanguard Medical Associates facilities.
cList of included antituberculous medications: isoniazid, ethambutol, rifampin, rifabutin, rifapentine, pyrazinamide, streptomycin, para-aminosalicylic acid, kanamycin, capreomycin, cycloserine, and ethionamide
dScreened for Common Procedural Technology (CPT) 84460 (LxComponent 3836, 3838, 3840), CPT 87116 (LxComponent 2785, 3021, 3836, 3838, 3840, 4694, 931), CPT 87206 (LxComponent 3761), and CPT 87556 (LxComponent 4598)
eAny occurrence of 0.3–0.6 as the fourth digit of an ICD-9 code between 010 and 018
PPV = positive predictive value
TB = tuberculosis
ICD-9 = International Classification of Diseases, Ninth Revision
AFB = acid-fast bacilli